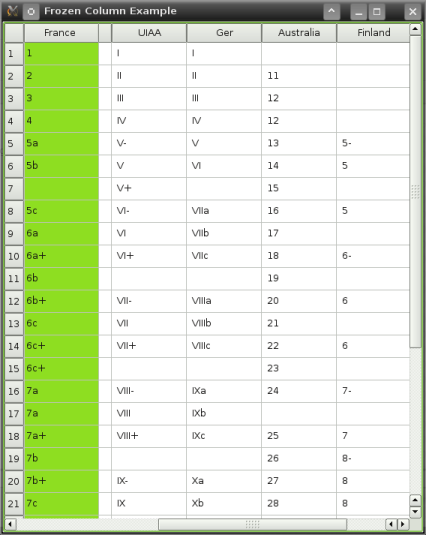
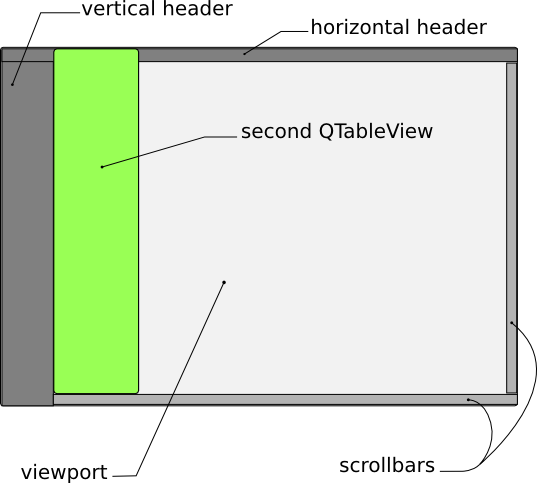
FreezeTableWidget Class Implementation
The constructor takes model as an argument and creates a table view that we will use to display the frozen column. Then, within the constructor, we invoke the init() function to set up the frozen column. Finally, we connect the QHeaderView::sectionResized() signals (for horizontal and vertical headers) to the appropriate slots. This ensures that our frozen column's sections are in sync with the headers. We also connect the vertical scrollbars together so that the frozen column scrolls vertically with the rest of our table.
FreezeTableWidget::FreezeTableWidget(QAbstractItemModel * model)
{
setModel(model);
frozenTableView = new QTableView(this);
init();
connect(horizontalHeader(),SIGNAL(sectionResized(int,int,int)), this,
SLOT(updateSectionWidth(int,int,int)));
connect(verticalHeader(),SIGNAL(sectionResized(int,int,int)), this,
SLOT(updateSectionHeight(int,int,int)));
connect(frozenTableView->verticalScrollBar(), SIGNAL(valueChanged(int)),
verticalScrollBar(), SLOT(setValue(int)));
connect(verticalScrollBar(), SIGNAL(valueChanged(int)),
frozenTableView->verticalScrollBar(), SLOT(setValue(int)));
}
In the init() function, we ensure that the overlay table view responsible for displaying the frozen column, is set up properly. This means that this table view, frozenTableView, has to have the same model as the main table view. However, the difference here is: frozenTableView's only visible column is its first column; we hide the others using setColumnHidden()
void FreezeTableWidget::init()
{
frozenTableView->setModel(model());
frozenTableView->setFocusPolicy(Qt::NoFocus);
frozenTableView->verticalHeader()->hide();
frozenTableView->horizontalHeader()->setResizeMode(QHeaderView::Fixed);
viewport()->stackUnder(frozenTableView);
In terms of the frozen column's z-order, we stack it on top of the viewport. This is achieved by calling stackUnder() on the viewport. For appearance's sake, we prevent the column from stealing focus from the main tableview. Also, we make sure that both views share the same selection model, so only one cell can be selected at a time. A few other tweaks are done to make our application look good and behave consistently with the main tableview. Note that we called updateFrozenTableGeometry() to make the column occupy the correct spot.
frozenTableView->setStyleSheet("QTableView { border: none;"
"background-color: #8EDE21;"
"selection-background-color: #999}");
frozenTableView->setSelectionModel(selectionModel());
for(int col=1; col<model()->columnCount(); col++)
frozenTableView->setColumnHidden(col, true);
frozenTableView->setColumnWidth(0, columnWidth(0) );
frozenTableView->setHorizontalScrollBarPolicy(Qt::ScrollBarAlwaysOff);
frozenTableView->setVerticalScrollBarPolicy(Qt::ScrollBarAlwaysOff);
frozenTableView->show();
updateFrozenTableGeometry();
setHorizontalScrollMode(ScrollPerPixel);
setVerticalScrollMode(ScrollPerPixel);
frozenTableView->setVerticalScrollMode(ScrollPerPixel);
}
When you resize the frozen column, the same column on the main table view must resize accordingly, to provide seamless integration. This is accomplished by getting the new size of the column from the newSize value from the sectionResized() signal, emitted by both the horizontal and vertical header.
void FreezeTableWidget::updateSectionWidth(int logicalIndex, int, int newSize)
{
if(logicalIndex==0){
frozenTableView->setColumnWidth(0,newSize);
updateFrozenTableGeometry();
}
}
void FreezeTableWidget::updateSectionHeight(int logicalIndex, int, int newSize)
{
frozenTableView->setRowHeight(logicalIndex, newSize);
}
Since the width of the frozen column is modified, we adjust the geometry of the widget accordingly by invoking updateFrozenTableGeometry(). This function is further explained below.
In our reimplementation of QTableView::resizeEvent(), we call updateFrozenTableGeometry() after invoking the base class implementation.
void FreezeTableWidget::resizeEvent(QResizeEvent * event)
{
QTableView::resizeEvent(event);
updateFrozenTableGeometry();
}
When navigating around the table with the keyboard, we need to ensure that the current selection does not disappear behind the frozen column. To synchronize this, we reimplement QTableView::moveCursor() and adjust the scrollbar positions if needed, after calling the base class implementation.
QModelIndex FreezeTableWidget::moveCursor(CursorAction cursorAction,
Qt::KeyboardModifiers modifiers)
{
QModelIndex current = QTableView::moveCursor(cursorAction, modifiers);
if(cursorAction == MoveLeft && current.column()>0
&& visualRect(current).topLeft().x() < frozenTableView->columnWidth(0) ){
const int newValue = horizontalScrollBar()->value() + visualRect(current).topLeft().x()
- frozenTableView->columnWidth(0);
horizontalScrollBar()->setValue(newValue);
}
return current;
}
The frozen column's geometry calculation is based on the geometry of the table underneath, so it always appears in the right place. Using the QFrame::frameWidth() function helps to calculate this geometry correctly, no matter which style is used. We rely on the geometry of the viewport and headers to set the boundaries for the frozen column.
void FreezeTableWidget::updateFrozenTableGeometry()
{
frozenTableView->setGeometry( verticalHeader()->width()+frameWidth(),
frameWidth(), columnWidth(0),
viewport()->height()+horizontalHeader()->height());
}