The Virtual Framebuffer |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -width <value> | The width of the virtual framebuffer (default: 240). |
| -height <value> | The height of the virtual framebuffer (default: 320). |
| -depth <value> | The depth of the virtual framebuffer (1, 8 or 32; default: 8). |
| -nocursor | Do not display the X11 cursor in the framebuffer window. |
| -qwsdisplay <:id> | The Qt for Embedded Linux display ID (default: 0). |
| -skin <name>.skin | The preferred skin. Note that the skin must be located in Qt's /tools/qvfb/ directory. |
| -zoom <factor> | Scales the application view with the given factor. |
Skins
A skin is a set of XML and pixmap files that tells the vitual framebuffer what it should look like and how it should behave; a skin can change the unrealistic default display into a display that is similar to the target device. To access the qvfb tool's menus when a skin is activated, right-click over the display.
Note that a skin can have buttons which (when clicked) send signals to the Qt Extended application running inside the virtual framebuffer, just as would happen on a real device.
| Target Device Environment The qvfb tool provides various skins by default, allowing the user to view their application in an environment similar to their target device. The provided skins are:
In addition, it is possible to create custom skins. |  |  |
Creating Custom Skins
The XML and pixmap files specifying a custom skin must be located in subdirectory of the Qt's /tools/qvfb directory, called /customskin.skin. See the ClamshellPhone skin for an example of the file structure:
cd path/to/Qt/tools/qvfb/ClamshellPhone.skin/
The /ClamshellPhone.skin directory contains the following files:
- ClamshellPhone.skin
- ClamshellPhone1-5.png
- ClamshellPhone1-5-pressed.png
- ClamshellPhone1-5-closed.png
- defaultbuttons.conf (only necessary for Qt Extended)
Note that the defaultbuttons.conf file is only necessary if the skin is supposed to be used with Qt Extended (The file customizes the launch screen applications, orders the soft keys and provides input method hints). See the Qt Extended documentation for more information.
| The ClamshellPhone Skin | ||
|---|---|---|
[SkinFile]
Up=ClamshellPhone1-5.png
Down=ClamshellPhone1-5-pressed.png
Closed=ClamshellPhone1-5-closed.png
Screen=72 84 176 208
Areas=22
"Power" 0x0100000a 205 563 249 586
"1" 0x0031 62 414 119 438
"2" 0x0032 130 414 189 438
"3" 0x0033 198 413 257 438
"4" 0x0034 54 444 117 470
"5" 0x0035 128 444 189 471
"6" 0x0036 202 444 264 471
"7" 0x0037 47 477 113 507
"8" 0x0038 126 477 190 507
"9" 0x0039 205 478 270 509
"*" 0x002a 39 515 110 552
"0" 0x0030 122 515 195 553
"#" 0x0023 207 516 280 553
"Context1" 0x01100000 137 360 108 383 123 410 90 409 60 387 63 378
100 362
"Back" 0x01000061 184 361 206 376 213 387 197 410 226 410 256 392
258 381 244 369
"Backspace" 0x01000003 68 563 113 587
"Select" 0x01010000 160 391 172 390 181 386 184 381 180 377 173
373 165 372 155 372 145 375 138 378 136
382 138 387 147 390
"Left" 0x1000012 141 390 136 385 136 381 143 375 132 371 120
380 121 393 129 401
"Down" 0x1000015 143 389 130 402 162 412 191 404 175 390
"Right" 0x1000014 186 370 176 375 184 382 182 387 175 390 190 404
201 396 202 375
"Up" 0x1000013 133 370 143 374 176 374 185 370 169 362 149 362
"Flip" 0x01100006 98 325 225 353
The ClamShellPhone.skin file quoted above, specifies three pixmaps: One for the normal skin (Up), one for the activated skin (Down) and one for the closed skin (Closed). In addition, it is possible to specify a pixmap for the cursor (using a Cursor variable). The file also specifies the screen size (Screen) and the number of available buttons (Areas). Then it describes the buttons themselves; each button is specified by its name, keycode and coordinates. The coordinates are a list of at least 2 points in clockwise order that define a shape for the button; a click inside this shape will be treated as a click on that button. While pressed, the pixels for the button are redrawn from the activated skin. | ||
 |  |  |
| ClamshellPhone1-5-closed.png | ClamshellPhone1-5.png | ClamshellPhone1-5-pressed.png |
The File Menu
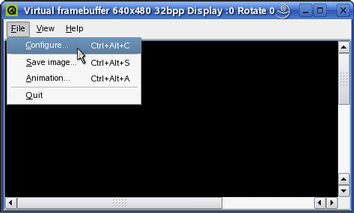
The File menu allows the user to configure the virtual framebuffer display (File|Configure...), save a snapshot of the framebuffer contents (File|Save Image...) and record the movements in the framebuffer (File|Animation...).
When choosing the File|Configure menu item, the qvfb tool provides a configuration dialog allowing the user to customize the display of the virtual framebuffer. The user can modify the size and depth as well as the Gamma values, and also select the preferred skin (i.e. making the virtual framebuffer simulate the target device environment). In addition, it is possible to emulate a touch screen and a LCD screen.
Note that when configuring (except when changing the Gamma values only), any applications using the virtual framebuffer will be terminated.
The View Menu
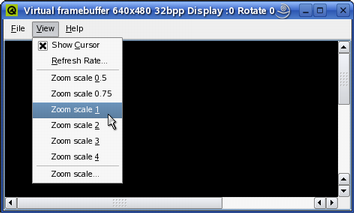
The View menu allows the user to modify the target's refresh rate (View|Refresh Rate...), making qvfb check for updated regions more or less frequently.
The regions of the display that have changed are updated periodically, i.e. the virtual framebuffer is displaying discrete snapshots of the framebuffer rather than each individual drawing operation. For this reason drawing problems such as flickering may not be apparent until the program is run using a real framebuffer. If little drawing is being done, the framebuffer will not show any updates between drawing events. If an application is displaying an animation, the updates will be frequent, and the application and qvfb will compete for processor time.
The View menu also allows the user to zoom the view of the application (View|Zoom *).
Running Applications Using the Virtual Framebuffer
Once the virtual framebuffer (the qvfb application) is running, it is ready for use: Start a server application (i.e. construct a QApplication object with the QApplication::GuiServer flag or use the -qws command line parameter. See the running applications documentation for details). For example:
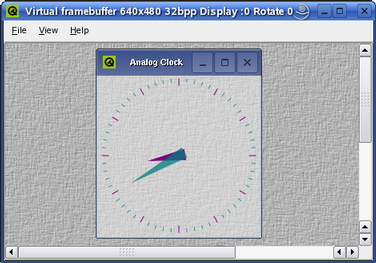
cd path/to/QtEmbedded/examples/widgets/analogclock make ./analogclock -qws
Note that as long as the virtual framebuffer is running and the current Qt for Embedded Linux configuration supports qvfb, Qt for Embedded Linux will automatically detect it and use it by default. Alternatively, the -display option can be used to specify the virtual framebuffer driver. For example:
cd path/to/QtEmbedded/examples/widgets/analogclock make ./analogclock -qws -display QVFb:0
Warning: If qvfb is not running (or the current Qt for Embedded Linux configuration doesn't support it) and the driver is not explicitly specified, Qt for Embedded Linux will write to the real framebuffer and the X11 display will be corrupted.
Best Of
Actualités les plus lues
- Pourquoi les programmeurs sont-ils moins payés que les gestionnaires de programmes ? Manquent-ils de pouvoir de négociation ? 45
- Les développeurs détestent-ils les antivirus ? Un programmeur manifeste sa haine envers ces solutions de sécurité 6
- Une nouvelle ère d'IHM 3D pour les automobiles, un concept proposé par Digia et implémenté avec Qt 2
- PySide devient un add-on Qt et rejoint le Qt Project et le modèle d'open gouvernance 1
- Interfaces mobiles : nouveaux usages, nouvelles ergonomies, par Miratech 0
- Qt Creator 2.5 est sorti en beta, l'EDI supporte maintenant plus de fonctionnalités de C++11 2
- Implémentation d'une table de hachage à référence faible avec Qt, un article de Christophe Dumez traduit par Thibaut Cuvelier 4
- « Quelque chose ne va vraiment pas avec les développeurs "modernes" », un développeur à "l'ancienne" critique la multiplication des bibliothèques 94
- Apercevoir la troisième dimension ou l'utilisation multithreadée d'OpenGL dans Qt, un article des Qt Quarterly traduit par Guillaume Belz 0
- Pourquoi les programmeurs sont-ils moins payés que les gestionnaires de programmes ? Manquent-ils de pouvoir de négociation ? 45
- Les développeurs ignorent-ils trop les failles découvertes dans leur code ? Prenez-vous en compte les remarques des autres ? 17
- Les développeurs détestent-ils les antivirus ? Un programmeur manifeste sa haine envers ces solutions de sécurité 6
- Quelles nouveautés de C++11 Visual C++ doit-il rapidement intégrer ? Donnez-nous votre avis 10
- Qt Commercial : Digia organise un webinar gratuit le 27 mars sur la conception d'interfaces utilisateur et d'applications avec le framework 0

- Linus Torvalds : le "C++ est un langage horrible", en justifiant le choix du C pour le système de gestion de version Git 100
- Comment prendre en compte l'utilisateur dans vos applications ? Pour un développeur, « 90 % des utilisateurs sont des idiots » 229
- Quel est LE livre que tout développeur doit lire absolument ? Celui qui vous a le plus marqué et inspiré 96
- Apple cède et s'engage à payer des droits à Nokia, le conflit des brevets entre les deux firmes s'achève 158
- Nokia porte à nouveau plainte contre Apple pour violation de sept nouveaux brevets 158
- Quel est le code dont vous êtes le plus fier ? Pourquoi l'avez-vous écrit ? Et pourquoi vous a-t-il donné autant de satisfaction ? 83
- Le Draft final de la norme C++ 0X validé 181

Le Qt Developer Network au hasard

Génération de bindings PySide avec Shiboken
Communauté
Ressources
- 91 cours et tutoriels Qt
- F.A.Q. Qt : 200 questions et réponses
- 48 Qt Quarterly, 35 Qt Labs et 22 Qt DevNet en français
- 43 outils Qt
- 99 sources Qt
- 26 binaires Qt
- 6 livres Qt et 9 critiques
- La documentation de Qt 4.7 en français : 157 classes, 70 concepts et 24 modules
- 3 certifications Qt
Liens utiles
Contact
- Vous souhaitez rejoindre la rédaction ou proposer un tutoriel, une traduction, une question... ? Postez dans le forum Contribuez ou contactez-nous par MP ou par email (voir en bas de page).
Qt dans le magazine
| Cette page est une traduction d'une page de la documentation de Qt, écrite par Nokia Corporation and/or its subsidiary(-ies). Les éventuels problèmes résultant d'une mauvaise traduction ne sont pas imputables à Nokia. | Qt 4.6-snapshot | |
| Copyright © 2012 Developpez LLC. Tous droits réservés Developpez LLC. Aucune reproduction, même partielle, ne peut être faite de ce site et de l'ensemble de son contenu : textes, documents et images sans l'autorisation expresse de Developpez LLC. Sinon, vous encourez selon la loi jusqu'à 3 ans de prison et jusqu'à 300 000 E de dommages et intérêts. Cette page est déposée à la SACD. | ||
| Vous avez déniché une erreur ? Un bug ? Une redirection cassée ? Ou tout autre problème, quel qu'il soit ? Ou bien vous désirez participer à ce projet de traduction ? N'hésitez pas à nous contacter ou par MP ! | ||
Copyright © 2000-2012 - www.developpez.com