QTransform Class Reference
|
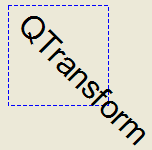 | void SimpleTransformation::paintEvent(QPaintEvent *)
{
QPainter painter(this);
painter.setPen(QPen(Qt::blue, 1, Qt::DashLine));
painter.drawRect(0, 0, 100, 100);
painter.rotate(45);
painter.setFont(QFont("Helvetica", 24));
painter.setPen(QPen(Qt::black, 1));
painter.drawText(20, 10, "QTransform");
}
|
Although these functions are very convenient, it can be more efficient to build a QTransform and call QPainter::setTransform() if you want to perform more than a single transform operation. For example:
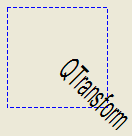 | void CombinedTransformation::paintEvent(QPaintEvent *)
{
QPainter painter(this);
painter.setPen(QPen(Qt::blue, 1, Qt::DashLine));
painter.drawRect(0, 0, 100, 100);
QTransform transform;
transform.translate(50, 50);
transform.rotate(45);
transform.scale(0.5, 1.0);
painter.setTransform(transform);
painter.setFont(QFont("Helvetica", 24));
painter.setPen(QPen(Qt::black, 1));
painter.drawText(20, 10, "QTransform");
}
|
Basic Matrix Operations
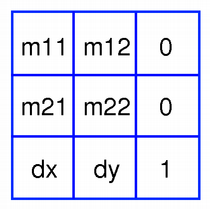
A QTransform object contains a 3 x 3 matrix. The dx and dy elements specify horizontal and vertical translation. The m11 and m22 elements specify horizontal and vertical scaling. And finally, the m21 and m12 elements specify horizontal and vertical shearing.
QTransform transforms a point in the plane to another point using the following formulas:
x' = m11*x + m21*y + dx y' = m22*y + m12*x + dy
The point (x, y) is the original point, and (x', y') is the transformed point. (x', y') can be transformed back to (x, y) by performing the same operation on the inverted() matrix.
The various matrix elements can be set when constructing the matrix, or by using the setMatrix() function later on. They also be manipulated using the translate(), rotate(), scale() and shear() convenience functions, The currently set values can be retrieved using the m11(), m12(), m21(), m22(), dx() and dy() functions.
Translation is the simplest transformation. Setting dx and dy will move the coordinate system dx units along the X axis and dy units along the Y axis. Scaling can be done by setting m11 and m22. For example, setting m11 to 2 and m22 to 1.5 will double the height and increase the width by 50%. The identity matrix has m11 and m22 set to 1 (all others are set to 0) mapping a point to itself. Shearing is controlled by m12 and m21. Setting these elements to values different from zero will twist the coordinate system. Rotation is achieved by carefully setting both the shearing factors and the scaling factors.
Here's the combined transformations example using basic matrix operations:
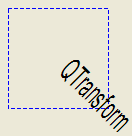 | void BasicOperations::paintEvent(QPaintEvent *)
{
double pi = 3.14;
double a = pi/180 * 45.0;
double sina = sin(a);
double cosa = cos(a);
QTransform translationTransform(1, 0, 0, 1, 50.0, 50.0);
QTransform rotationTransform(cosa, sina, -sina, cosa, 0, 0);
QTransform scalingTransform(0.5, 0, 0, 1.0, 0, 0);
QTransform transform;
transform = scalingTransform * rotationTransform * translationTransform;
QPainter painter(this);
painter.setPen(QPen(Qt::blue, 1, Qt::DashLine));
painter.drawRect(0, 0, 100, 100);
painter.setTransform(transform);
painter.setFont(QFont("Helvetica", 24));
painter.setPen(QPen(Qt::black, 1));
painter.drawText(20, 10, "QTransform");
}
|
See also QPainter, The Coordinate System, Affine Transformations Demo, and Transformations Example.
Member Type Documentation
enum QTransform::TransformationType
| Constant | Value |
|---|---|
| QTransform::TxNone | 0x00 |
| QTransform::TxTranslate | 0x01 |
| QTransform::TxScale | 0x02 |
| QTransform::TxRotate | 0x04 |
| QTransform::TxShear | 0x08 |
| QTransform::TxProject | 0x10 |
Member Function Documentation
QTransform::QTransform ()
Constructs an identity matrix.
All elements are set to zero except m11 and m22 (specifying the scale) and m13 which are set to 1.
See also reset().
QTransform::QTransform ( qreal h11, qreal h12, qreal h13, qreal h21, qreal h22, qreal h23, qreal h31, qreal h32, qreal h33 = 1.0 )
Constructs a matrix with the elements, h11, h12, h13, h21, h22, h23, h31, h32, h33.
See also setMatrix().
QTransform::QTransform ( qreal h11, qreal h12, qreal h21, qreal h22, qreal dx, qreal dy )
Constructs a matrix with the elements, h11, h12, h21, h22, dx and dy.
See also setMatrix().
QTransform::QTransform ( const QMatrix & matrix )
Constructs a matrix that is a copy of the given matrix. Note that the m13, m23, and m33 elements are set to 0, 0, and 1 respectively.
qreal QTransform::m11 () const
Returns the horizontal scaling factor.
See also scale() and Basic Matrix Operations.
qreal QTransform::m12 () const
Returns the vertical shearing factor.
See also shear() and Basic Matrix Operations.
qreal QTransform::m13 () const
Returns the horizontal projection factor.
See also translate() and Basic Matrix Operations.
qreal QTransform::m21 () const
Returns the horizontal shearing factor.
See also shear() and Basic Matrix Operations.
qreal QTransform::m22 () const
Returns the vertical scaling factor.
See also scale() and Basic Matrix Operations.
qreal QTransform::m23 () const
Returns the vertical projection factor.
See also translate() and Basic Matrix Operations.
qreal QTransform::m31 () const
Returns the horizontal translation factor.
See also dx(), translate(), and Basic Matrix Operations.
qreal QTransform::m32 () const
Returns the vertical translation factor.
See also dy(), translate(), and Basic Matrix Operations.
qreal QTransform::m33 () const
Returns the division factor.
See also translate() and Basic Matrix Operations.
QTransform QTransform::adjoint () const
Returns the adjoint of this matrix.
qreal QTransform::det () const
Returns the matrix's determinant.
qreal QTransform::determinant () const
Returns the matrix's determinant.
qreal QTransform::dx () const
Returns the horizontal translation factor.
See also m31(), translate(), and Basic Matrix Operations.
qreal QTransform::dy () const
Returns the vertical translation factor.
See also translate() and Basic Matrix Operations.
QTransform QTransform::inverted ( bool * invertible = 0 ) const
Returns an inverted copy of this matrix.
If the matrix is singular (not invertible), the returned matrix is the identity matrix. If invertible is valid (i.e. not 0), its value is set to true if the matrix is invertible, otherwise it is set to false.
See also isInvertible().
bool QTransform::isAffine () const
Returns true if the matrix represent an affine transformation, otherwise returns false.
bool QTransform::isIdentity () const
Returns true if the matrix is the identity matrix, otherwise returns false.
See also reset().
bool QTransform::isInvertible () const
Returns true if the matrix is invertible, otherwise returns false.
See also inverted().
bool QTransform::isRotating () const
Returns true if the matrix represents some kind of a rotating transformation, otherwise returns false.
See also reset().
bool QTransform::isScaling () const
Returns true if the matrix represents a scaling transformation, otherwise returns false.
See also reset().
bool QTransform::isTranslating () const
Returns true if the matrix represents a translating transformation, otherwise returns false.
See also reset().
void QTransform::map ( qreal x, qreal y, qreal * tx, qreal * ty ) const
Maps the given coordinates x and y into the coordinate system defined by this matrix. The resulting values are put in *tx and *ty, respectively.
The coordinates are transformed using the following formulas:
x' = m11*x + m21*y + dx y' = m22*y + m12*x + dy
The point (x, y) is the original point, and (x', y') is the transformed point.
See also Basic Matrix Operations.
QPointF QTransform::map ( const QPointF & p ) const
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Creates and returns a QPointF object that is a copy of the given point, p, mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix.
QPoint QTransform::map ( const QPoint & point ) const
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Creates and returns a QPoint object that is a copy of the given point, mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix. Note that the transformed coordinates are rounded to the nearest integer.
QLine QTransform::map ( const QLine & l ) const
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Creates and returns a QLineF object that is a copy of the given line, l, mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix.
QLineF QTransform::map ( const QLineF & line ) const
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Creates and returns a QLine object that is a copy of the given line, mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix. Note that the transformed coordinates are rounded to the nearest integer.
QPolygonF QTransform::map ( const QPolygonF & polygon ) const
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Creates and returns a QPolygonF object that is a copy of the given polygon, mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix.
QPolygon QTransform::map ( const QPolygon & polygon ) const
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Creates and returns a QPolygon object that is a copy of the given polygon, mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix. Note that the transformed coordinates are rounded to the nearest integer.
QRegion QTransform::map ( const QRegion & region ) const
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Creates and returns a QRegion object that is a copy of the given region, mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix.
Calling this method can be rather expensive if rotations or shearing are used.
QPainterPath QTransform::map ( const QPainterPath & path ) const
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Creates and returns a QPainterPath object that is a copy of the given path, mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix.
void QTransform::map ( int x, int y, int * tx, int * ty ) const
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Maps the given coordinates x and y into the coordinate system defined by this matrix. The resulting values are put in *tx and *ty, respectively. Note that the transformed coordinates are rounded to the nearest integer.
QRectF QTransform::mapRect ( const QRectF & rectangle ) const
Creates and returns a QRectF object that is a copy of the given rectangle, mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix.
The rectangle's coordinates are transformed using the following formulas:
x' = m11*x + m21*y + dx
y' = m22*y + m12*x + dy
if (is not affine) {
w' = m13*x + m23*y + m33
x' /= w'
y' /= w'
}
If rotation or shearing has been specified, this function returns the bounding rectangle. To retrieve the exact region the given rectangle maps to, use the mapToPolygon() function instead.
See also mapToPolygon() and Basic Matrix Operations.
QRect QTransform::mapRect ( const QRect & rectangle ) const
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Creates and returns a QRect object that is a copy of the given rectangle, mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix. Note that the transformed coordinates are rounded to the nearest integer.
QPolygon QTransform::mapToPolygon ( const QRect & rectangle ) const
Creates and returns a QPolygon representation of the given rectangle, mapped into the coordinate system defined by this matrix.
The rectangle's coordinates are transformed using the following formulas:
x' = m11*x + m21*y + dx
y' = m22*y + m12*x + dy
if (is not affine) {
w' = m13*x + m23*y + m33
x' /= w'
y' /= w'
}
Polygons and rectangles behave slightly differently when transformed (due to integer rounding), so matrix.map(QPolygon(rectangle)) is not always the same as matrix.mapToPolygon(rectangle).
See also mapRect() and Basic Matrix Operations.
bool QTransform::quadToQuad ( const QPolygonF & one, const QPolygonF & two, QTransform & trans ) [static]
Creates a transformation matrix, trans, that maps a four-sided polygon, one, to another four-sided polygon, two. Returns true if the transformation is possible; otherwise returns false.
This is a convenience method combining quadToSquare() and squareToQuad() methods. It allows the input quad to be transformed into any other quad.
See also squareToQuad() and quadToSquare().
bool QTransform::quadToSquare ( const QPolygonF & quad, QTransform & trans ) [static]
Creates a transformation matrix, trans, that maps a four-sided polygon, quad, to a unit square. Returns true if the transformation is constructed or false if such a transformation does not exist.
See also squareToQuad() and quadToQuad().
void QTransform::reset ()
Resets the matrix to an identity matrix, i.e. all elements are set to zero, except m11 and m22 (specifying the scale) which are set to 1.
See also QTransform(), isIdentity(), and Basic Matrix Operations.
QTransform & QTransform::rotate ( qreal angle, Qt::Axis axis = Qt::ZAxis )
Rotates the coordinate system counterclockwise by the given angle about the specified axis and returns a reference to the matrix.
Note that if you apply a QTransform to a point defined in widget coordinates, the direction of the rotation will be clockwise because the y-axis points downwards.
The angle is specified in degrees.
See also setMatrix().
QTransform & QTransform::rotateRadians ( qreal angle, Qt::Axis axis = Qt::ZAxis )
Rotates the coordinate system counterclockwise by the given angle about the specified axis and returns a reference to the matrix.
Note that if you apply a QTransform to a point defined in widget coordinates, the direction of the rotation will be clockwise because the y-axis points downwards.
The angle is specified in radians.
See also setMatrix().
QTransform & QTransform::scale ( qreal sx, qreal sy )
Scales the coordinate system by sx horizontally and sy vertically, and returns a reference to the matrix.
See also setMatrix().
void QTransform::setMatrix ( qreal m11, qreal m12, qreal m13, qreal m21, qreal m22, qreal m23, qreal m31, qreal m32, qreal m33 )
Sets the matrix elements to the specified values, m11, m12, m13 m21, m22, m23 m31, m32 and m33. Note that this function replaces the previous values. QMatrix provides the translate(), rotate(), scale() and shear() convenience functions to manipulate the various matrix elements based on the currently defined coordinate system.
See also QTransform().
QTransform & QTransform::shear ( qreal sh, qreal sv )
Shears the coordinate system by sh horizontally and sv vertically, and returns a reference to the matrix.
See also setMatrix().
bool QTransform::squareToQuad ( const QPolygonF & quad, QTransform & trans ) [static]
Creates a transformation matrix, trans, that maps a unit square to a four-sided polygon, quad. Returns true if the transformation is constructed or false if such a transformation does not exist.
See also quadToSquare() and quadToQuad().
const QMatrix & QTransform::toAffine () const
Returns the QTransform cast to a QMatrix.
QTransform & QTransform::translate ( qreal dx, qreal dy )
Moves the coordinate system dx along the x axis and dy along the y axis, and returns a reference to the matrix.
See also setMatrix().
QTransform QTransform::transposed () const
Returns the transpose of this matrix.
TransformationType QTransform::type () const
Returns the transformation type of this matrix.
QTransform::operator QVariant () const
Returns the transform as a QVariant.
bool QTransform::operator!= ( const QTransform & matrix ) const
Returns true if this matrix is not equal to the given matrix, otherwise returns false.
QTransform QTransform::operator* ( const QTransform & matrix ) const
Returns the result of multiplying this matrix by the given matrix.
Note that matrix multiplication is not commutative, i.e. a*b != b*a.
QTransform & QTransform::operator*= ( const QTransform & matrix )
Returns the result of multiplying this matrix by the given matrix.
QTransform & QTransform::operator*= ( qreal scalar )
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Returns the result of performing an element-wise multiplication of this matrix with the given scalar.
QTransform & QTransform::operator+= ( qreal scalar )
Returns the matrix obtained by adding the given scalar to each element of this matrix.
QTransform & QTransform::operator-= ( qreal scalar )
Returns the matrix obtained by subtracting the given scalar from each element of this matrix.
QTransform & QTransform::operator/= ( qreal scalar )
Returns the result of performing an element-wise division of this matrix by the given scalar.
QTransform & QTransform::operator= ( const QTransform & matrix )
Assigns the given matrix's values to this matrix.
bool QTransform::operator== ( const QTransform & matrix ) const
Returns true if this matrix is equal to the given matrix, otherwise returns false.
Related Non-Members
QPoint operator* ( const QPoint & point, const QTransform & matrix )
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
This is the same as matrix.map(point).
See also QTransform::map().
QPointF operator* ( const QPointF & point, const QTransform & matrix )
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Same as matrix.map(point).
See also QTransform::map().
QLineF operator* ( const QLineF & line, const QTransform & matrix )
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
This is the same as matrix.map(line).
See also QTransform::map().
QLine operator* ( const QLine & line, const QTransform & matrix )
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
This is the same as matrix.map(line).
See also QTransform::map().
QPolygon operator* ( const QPolygon & polygon, const QTransform & matrix )
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
This is the same as matrix.map(polygon).
See also QTransform::map().
QPolygonF operator* ( const QPolygonF & polygon, const QTransform & matrix )
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
This is the same as matrix.map(polygon).
This function was introduced in Qt 4.3.
See also QTransform::map().
QRegion operator* ( const QRegion & region, const QTransform & matrix )
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
This is the same as matrix.map(region).
See also QTransform::map().
QPainterPath operator* ( const QPainterPath & path, const QTransform & matrix )
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
This is the same as matrix.map(path).
This function was introduced in Qt 4.3.
See also QTransform::map().
QDataStream & operator<< ( QDataStream & stream, const QTransform & matrix )
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Writes the given matrix to the given stream and returns a reference to the stream.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.3.
See also Format of the QDataStream Operators.
QDataStream & operator>> ( QDataStream & stream, QTransform & matrix )
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience.
Reads the given matrix from the given stream and returns a reference to the stream.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.3.
See also Format of the QDataStream Operators.
Best Of
Actualités les plus lues
- Pourquoi les programmeurs sont-ils moins payés que les gestionnaires de programmes ? Manquent-ils de pouvoir de négociation ? 42
- Qt Commercial : Digia organise un webinar gratuit le 27 mars sur la conception d'interfaces utilisateur et d'applications avec le framework 0
- Interfaces mobiles : nouveaux usages, nouvelles ergonomies, par Miratech 0
- Implémentation d'une table de hachage à référence faible avec Qt, un article de Christophe Dumez traduit par Thibaut Cuvelier 4
- « Quelque chose ne va vraiment pas avec les développeurs "modernes" », un développeur à "l'ancienne" critique la multiplication des bibliothèques 94
- Apercevoir la troisième dimension ou l'utilisation multithreadée d'OpenGL dans Qt, un article des Qt Quarterly traduit par Guillaume Belz 0
- Les développeurs ignorent-ils trop les failles découvertes dans leur code ? Prenez-vous en compte les remarques des autres ? 17
- Pourquoi les programmeurs sont-ils moins payés que les gestionnaires de programmes ? Manquent-ils de pouvoir de négociation ? 42
- Quelles nouveautés de C++11 Visual C++ doit-il rapidement intégrer ? Donnez-nous votre avis 10
- Adieu qmake, bienvenue qbs : Qt Building Suite, un outil déclaratif et extensible pour la compilation de projets Qt 17
- 2017 : un quinquennat pour une nouvelle version du C++ ? Possible, selon Herb Sutter 7

- Linus Torvalds : le "C++ est un langage horrible", en justifiant le choix du C pour le système de gestion de version Git 100
- Comment prendre en compte l'utilisateur dans vos applications ? Pour un développeur, « 90 % des utilisateurs sont des idiots » 229
- Quel est LE livre que tout développeur doit lire absolument ? Celui qui vous a le plus marqué et inspiré 96
- Apple cède et s'engage à payer des droits à Nokia, le conflit des brevets entre les deux firmes s'achève 158
- Nokia porte à nouveau plainte contre Apple pour violation de sept nouveaux brevets 158
- Quel est le code dont vous êtes le plus fier ? Pourquoi l'avez-vous écrit ? Et pourquoi vous a-t-il donné autant de satisfaction ? 83
- Le Draft final de la norme C++ 0X validé 181

Le Qt Quarterly au hasard

Un plugin pour QImage
Communauté
Ressources
- 91 cours et tutoriels Qt
- F.A.Q. Qt : 200 questions et réponses
- 48 Qt Quarterly, 35 Qt Labs et 22 Qt DevNet en français
- 43 outils Qt
- 99 sources Qt
- 26 binaires Qt
- 6 livres Qt et 9 critiques
- La documentation de Qt 4.7 en français : 157 classes, 70 concepts et 24 modules
- 3 certifications Qt
Liens utiles
Contact
- Vous souhaitez rejoindre la rédaction ou proposer un tutoriel, une traduction, une question... ? Postez dans le forum Contribuez ou contactez-nous par MP ou par email (voir en bas de page).
Qt dans le magazine
| Cette page est une traduction d'une page de la documentation de Qt, écrite par Nokia Corporation and/or its subsidiary(-ies). Les éventuels problèmes résultant d'une mauvaise traduction ne sont pas imputables à Nokia. | Qt qtextended4.4 | |
| Copyright © 2012 Developpez LLC. Tous droits réservés Developpez LLC. Aucune reproduction, même partielle, ne peut être faite de ce site et de l'ensemble de son contenu : textes, documents et images sans l'autorisation expresse de Developpez LLC. Sinon, vous encourez selon la loi jusqu'à 3 ans de prison et jusqu'à 300 000 E de dommages et intérêts. Cette page est déposée à la SACD. | ||
| Vous avez déniché une erreur ? Un bug ? Une redirection cassée ? Ou tout autre problème, quel qu'il soit ? Ou bien vous désirez participer à ce projet de traduction ? N'hésitez pas à nous contacter ou par MP ! | ||
Copyright © 2000-2012 - www.developpez.com



















