Widgets Tutorial
|
QWidget *window = new QWidget();
window->resize(320, 240);
window->show();
|
|
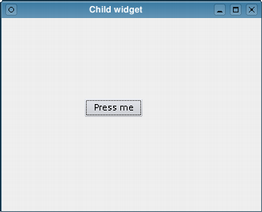
We can add a child widget to this window by passing window as the parent to its constructor. In this case, we add a button to the window and place it in a specific location:
QPushButton *button = new QPushButton(tr("Press me"), window);
button->move(100, 100);
button->show();
|
|
The button is now a child of the window and will be deleted when the window is destroyed. Note that hiding or closing the window does not automatically destroy it.
Using Layouts
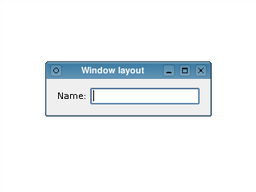
Usually, child widgets are arranged inside a window using layout objects rather than by specifying positions and sizes explicitly. Here, we construct a label and line edit widget that we would like to arrange side-by-side.
QLabel *label = new QLabel(tr("Name:"));
QLineEdit *lineEdit = new QLineEdit();
QHBoxLayout *layout = new QHBoxLayout();
layout->addWidget(label);
layout->addWidget(lineEdit);
window->setLayout(layout);
|
|
The layout object we construct manages the positions and sizes of widgets supplied to it with the addWidget() function. The layout itself is supplied to the window itself in the call to setLayout(). Layouts are only visible through the effects they have on the widgets (and other layouts) they are responsible for managing.
In the example above, the ownership of each widget is not immediately clear. Since we construct the widgets and the layout without parent objects, we would expect to see an empty window and two separate windows containing a label and a line edit. However, when we tell the layout to manage the label and line edit and set the layout on the window, both the widgets and the layout itself are ''reparented'' to become children of the window.
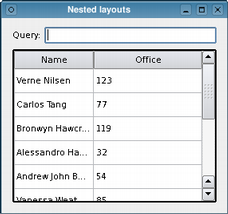
Just as widgets can contain other widgets, layouts can be used to provide different levels of grouping for widgets. Here, we want to display a label alongside a line edit at the top of a window, above a table view showing the results of a query.
QLabel *queryLabel = new QLabel(tr("Query:"));
QLineEdit *queryEdit = new QLineEdit();
QTableView *resultView = new QTableView();
QHBoxLayout *queryLayout = new QHBoxLayout();
queryLayout->addWidget(queryLabel);
queryLayout->addWidget(queryEdit);
QVBoxLayout *mainLayout = new QVBoxLayout();
mainLayout->addLayout(queryLayout);
mainLayout->addWidget(resultView);
window->setLayout(mainLayout);
|
|
As well as QHBoxLayout and QVBoxLayout, Qt also provides QGridLayout and QFormLayout classes to help with more complex user interfaces.
| Cette page est une traduction d'une page de la documentation de Qt, écrite par Nokia Corporation and/or its subsidiary(-ies). Les éventuels problèmes résultant d'une mauvaise traduction ne sont pas imputables à Nokia. | Qt qtextended4.4 | |
| Copyright © 2012 Developpez LLC. Tous droits réservés Developpez LLC. Aucune reproduction, même partielle, ne peut être faite de ce site et de l'ensemble de son contenu : textes, documents et images sans l'autorisation expresse de Developpez LLC. Sinon, vous encourez selon la loi jusqu'à 3 ans de prison et jusqu'à 300 000 E de dommages et intérêts. Cette page est déposée à la SACD. | ||
| Vous avez déniché une erreur ? Un bug ? Une redirection cassée ? Ou tout autre problème, quel qu'il soit ? Ou bien vous désirez participer à ce projet de traduction ? N'hésitez pas à nous contacter ou par MP ! | ||
Copyright © 2000-2012 - www.developpez.com