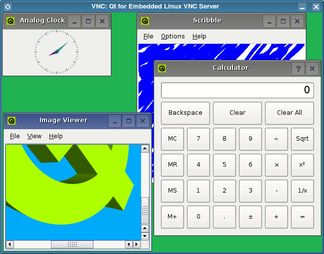
The VNC Protocol and Qt for Embedded Linux |
| The Virtual Framebuffer The virtual framebuffer is an alternative technique recommended for development and debugging purposes. The virtual framebuffer emulates a framebuffer using a shared memory region and the qvfb tool to display the framebuffer in a window. Its use of shared memory makes the virtual framebuffer much faster and smoother than using the VNC protocol, but it does not operate over a network. | 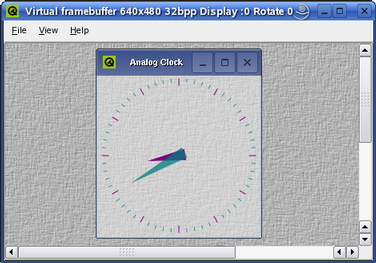 |
Best Of
Actualités les plus lues
- « Quelque chose ne va vraiment pas avec les développeurs "modernes" », un développeur à "l'ancienne" critique la multiplication des bibliothèques 53
- Créer des applications avec un style Metro avec Qt, exemples en QML et C++, un article du blog Digia traduit par Thibaut Cuvelier 0
- Orientation de l'écran en QML, un article de Christophe Dumez traduit par Thibaut Cuvelier 0
- « Quelque chose ne va vraiment pas avec les développeurs "modernes" », un développeur à "l'ancienne" critique la multiplication des bibliothèques 53
- Les développeurs ignorent-ils trop les failles découvertes dans leur code ? Prenez-vous en compte les remarques des autres ? 17
- Apercevoir la troisième dimension ou l'utilisation multithreadée d'OpenGL dans Qt, un article des Qt Quarterly traduit par Guillaume Belz 0
- BlackBerry 10 : premières images du prochain OS de RIM qui devrait intégrer des widgets et des tuiles inspirées de Windows Phone 0
- Quelles nouveautés de C++11 Visual C++ doit-il rapidement intégrer ? Donnez-nous votre avis 10
- Adieu qmake, bienvenue qbs : Qt Building Suite, un outil déclaratif et extensible pour la compilation de projets Qt 17
- La rubrique Qt a besoin de vous ! 1

- Linus Torvalds : le "C++ est un langage horrible", en justifiant le choix du C pour le système de gestion de version Git 100
- Comment prendre en compte l'utilisateur dans vos applications ? Pour un développeur, « 90 % des utilisateurs sont des idiots » 229
- Quel est LE livre que tout développeur doit lire absolument ? Celui qui vous a le plus marqué et inspiré 96
- Apple cède et s'engage à payer des droits à Nokia, le conflit des brevets entre les deux firmes s'achève 158
- Nokia porte à nouveau plainte contre Apple pour violation de sept nouveaux brevets 158
- Quel est le code dont vous êtes le plus fier ? Pourquoi l'avez-vous écrit ? Et pourquoi vous a-t-il donné autant de satisfaction ? 83
- Le Draft final de la norme C++ 0X validé 181

Le Qt Quarterly au hasard

Implémenter un mutex en lecture et en écriture
Communauté
Ressources
- 91 cours et tutoriels Qt
- F.A.Q. Qt : 200 questions et réponses
- 48 Qt Quarterly, 35 Qt Labs et 22 Qt DevNet en français
- 43 outils Qt
- 99 sources Qt
- 26 binaires Qt
- 6 livres Qt et 9 critiques
- La documentation de Qt 4.7 en français : 157 classes, 70 concepts et 24 modules
- 3 certifications Qt
Liens utiles
Contact
- Vous souhaitez rejoindre la rédaction ou proposer un tutoriel, une traduction, une question... ? Postez dans le forum Contribuez ou contactez-nous par MP ou par email (voir en bas de page).
Qt dans le magazine
| Cette page est une traduction d'une page de la documentation de Qt, écrite par Nokia Corporation and/or its subsidiary(-ies). Les éventuels problèmes résultant d'une mauvaise traduction ne sont pas imputables à Nokia. | Qt 4.4 | |
| Copyright © 2012 Developpez LLC. Tous droits réservés Developpez LLC. Aucune reproduction, même partielle, ne peut être faite de ce site et de l'ensemble de son contenu : textes, documents et images sans l'autorisation expresse de Developpez LLC. Sinon, vous encourez selon la loi jusqu'à 3 ans de prison et jusqu'à 300 000 E de dommages et intérêts. Cette page est déposée à la SACD. | ||
| Vous avez déniché une erreur ? Un bug ? Une redirection cassée ? Ou tout autre problème, quel qu'il soit ? Ou bien vous désirez participer à ce projet de traduction ? N'hésitez pas à nous contacter ou par MP ! | ||
Copyright © 2000-2012 - www.developpez.com