QSortFilterProxyModel Class Reference |
|
|
- 1 property inherited from QObject
Public Functions
- QSortFilterProxyModel ( QObject * parent = 0 )
- ~QSortFilterProxyModel ()
- bool dynamicSortFilter () const
- Qt::CaseSensitivity filterCaseSensitivity () const
- int filterKeyColumn () const
- QRegExp filterRegExp () const
- int filterRole () const
- bool isSortLocaleAware () const
- virtual QModelIndex mapFromSource ( const QModelIndex & sourceIndex ) const
- virtual QModelIndex mapToSource ( const QModelIndex & proxyIndex ) const
- void setDynamicSortFilter ( bool enable )
- void setFilterCaseSensitivity ( Qt::CaseSensitivity cs )
- void setFilterKeyColumn ( int column )
- void setFilterRegExp ( const QRegExp & regExp )
- void setFilterRole ( int role )
- void setSortCaseSensitivity ( Qt::CaseSensitivity cs )
- void setSortLocaleAware ( bool on )
- void setSortRole ( int role )
- Qt::CaseSensitivity sortCaseSensitivity () const
- int sortColumn () const
- Qt::SortOrder sortOrder () const
- int sortRole () const
- 6 public functions inherited from QAbstractProxyModel
- 34 public functions inherited from QAbstractItemModel
- 29 public functions inherited from QObject
Public Slots
- void invalidate ()
- void setFilterFixedString ( const QString & pattern )
- void setFilterRegExp ( const QString & pattern )
- void setFilterWildcard ( const QString & pattern )
- 2 public slots inherited from QAbstractItemModel
- 1 public slot inherited from QObject
Protected Functions
- virtual bool filterAcceptsColumn ( int source_column, const QModelIndex & source_parent ) const
- virtual bool filterAcceptsRow ( int source_row, const QModelIndex & source_parent ) const
- void invalidateFilter ()
- virtual bool lessThan ( const QModelIndex & left, const QModelIndex & right ) const
- 14 protected functions inherited from QAbstractItemModel
- 7 protected functions inherited from QObject
Additional Inherited Members
- 14 signals inherited from QAbstractItemModel
- 1 signal inherited from QObject
- 5 static public members inherited from QObject
Detailed Description
The QSortFilterProxyModel class provides support for sorting and filtering data passed between another model and a view.
QSortFilterProxyModel can be used for sorting items, filtering out items, or both. The model transforms the structure of a source model by mapping the model indexes it supplies to new indexes, corresponding to different locations, for views to use. This approach allows a given source model to be restructured as far as views are concerned without requiring any transformations on the underlying data, and without duplicating the data in memory.
Let's assume that we want to sort and filter the items provided by a custom model. The code to set up the model and the view, without sorting and filtering, would look like this:
QTreeView *treeView = new QTreeView;
MyItemModel *model = new MyItemModel(this);
treeView->setModel(model);
To add sorting and filtering support to MyItemModel, we need to create a QSortFilterProxyModel, call setSourceModel() with the MyItemModel as argument, and install the QSortFilterProxyModel on the view:
QTreeView *treeView = new QTreeView;
MyItemModel *sourceModel = new MyItemModel(this);
QSortFilterProxyModel *proxyModel = new QSortFilterProxyModel(this);
proxyModel->setSourceModel(sourceModel);
treeView->setModel(proxyModel);
At this point, neither sorting nor filtering is enabled; the original data is displayed in the view. Any changes made through the QSortFilterProxyModel are applied to the original model.
The QSortFilterProxyModel acts as a wrapper for the original model. If you need to convert source QModelIndexes to sorted/filtered model indexes or vice versa, use mapToSource(), mapFromSource(), mapSelectionToSource(), and mapSelectionFromSource().
Note: By default, the model does not dynamically re-sort and re-filter data whenever the original model changes. This behavior can be changed by setting the dynamicSortFilter property.
The Basic Sort/Filter Model and Custom Sort/Filter Model examples illustrate how to use QSortFilterProxyModel to perform basic sorting and filtering and how to subclass it to implement custom behavior.
Sorting
QTableView and QTreeView have a sortingEnabled property that controls whether the user can sort the view by clicking the view's horizontal header. For example:
treeView->setSortingEnabled(true);
When this feature is on (the default is off), clicking on a header section sorts the items according to that column. By clicking repeatedly, the user can alternate between ascending and descending order.
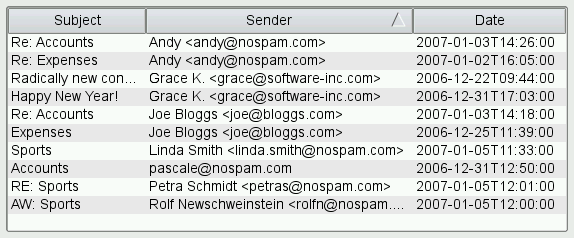
Behind the scene, the view calls the sort() virtual function on the model to reorder the data in the model. To make your data sortable, you can either implement sort() in your model, or you use a QSortFilterProxyModel to wrap your model -- QSortFilterProxyModel provides a generic sort() reimplementation that operates on the sortRole() (Qt::DisplayRole by default) of the items and that understands several data types, including int, QString, and QDateTime. For hierarchical models, sorting is applied recursively to all child items. String comparisons are case sensitive by default; this can be changed by setting the sortCaseSensitivity property.
Custom sorting behavior is achieved by subclassing QSortFilterProxyModel and reimplementing lessThan(), which is used to compare items. For example:
bool MySortFilterProxyModel::lessThan(const QModelIndex &left,
const QModelIndex &right) const
{
QVariant leftData = sourceModel()->data(left);
QVariant rightData = sourceModel()->data(right);
if (leftData.type() == QVariant::DateTime) {
return leftData.toDateTime() < rightData.toDateTime();
} else {
QRegExp *emailPattern = new QRegExp("([\\w\\.]*@[\\w\\.]*)");
QString leftString = leftData.toString();
if(left.column() == 1 && emailPattern->indexIn(leftString) != -1)
leftString = emailPattern->cap(1);
QString rightString = rightData.toString();
if(right.column() == 1 && emailPattern->indexIn(rightString) != -1)
rightString = emailPattern->cap(1);
return QString::localeAwareCompare(leftString, rightString) < 0;
}
}
(This code snippet comes from the Custom Sort/Filter Model example.)
An alternative approach to sorting is to disable sorting on the view and to impose a certain order to the user. This is done by explicitly calling sort() with the desired column and order as arguments on the QSortFilterProxyModel (or on the original model if it implements sort()). For example:
proxyModel->sort(2, Qt::AscendingOrder);
QSortFilterProxyModel can be sorted by column -1, in which case it returns to the sort order of the underlying source model.
Filtering
In addition to sorting, QSortFilterProxyModel can be used to hide items that don't match a certain filter. The filter is specified using a QRegExp object and is applied to the filterRole() (Qt::DisplayRole by default) of each item, for a given column. The QRegExp object can be used to match a regular expression, a wildcard pattern, or a fixed string. For example:
proxyModel->setFilterRegExp(QRegExp(".png", Qt::CaseInsensitive,
QRegExp::FixedString));
proxyModel->setFilterKeyColumn(1);
For hierarchical models, the filter is applied recursively to all children. If a parent item doesn't match the filter, none of its children will be shown.
A common use case is to let the user specify the filter regexp, wildcard pattern, or fixed string in a QLineEdit and to connect the textChanged() signal to setFilterRegExp(), setFilterWildcard(), or setFilterFixedString() to reapply the filter.
Custom filtering behavior can be achieved by reimplementing the filterAcceptsRow() and filterAcceptsColumn() functions. For example, the following implementation ignores the filterKeyColumn property and performs filtering on columns 0, 1, and 2:
bool MySortFilterProxyModel::filterAcceptsRow(int sourceRow,
const QModelIndex &sourceParent) const
{
QModelIndex index0 = sourceModel()->index(sourceRow, 0, sourceParent);
QModelIndex index1 = sourceModel()->index(sourceRow, 1, sourceParent);
QModelIndex index2 = sourceModel()->index(sourceRow, 2, sourceParent);
return (sourceModel()->data(index0).toString().contains(filterRegExp())
|| sourceModel()->data(index1).toString().contains(filterRegExp()))
&& dateInRange(sourceModel()->data(index2).toDate());
}
(This code snippet comes from the Custom Sort/Filter Model example.)
If you are working with large amounts of filtering and have to invoke invalidateFilter() repeatedly, using reset() may be more efficient, depending on the implementation of your model. However, note that reset() returns the proxy model to its original state, losing selection information, and will cause the proxy model to be repopulated.
Subclassing
Note: Some general guidelines for subclassing models are available in the Model Subclassing Reference.
Since QAbstractProxyModel and its subclasses are derived from QAbstractItemModel, much of the same advice about subclassing normal models also applies to proxy models. In addition, it is worth noting that many of the default implementations of functions in this class are written so that they call the equivalent functions in the relevant source model. This simple proxying mechanism may need to be overridden for source models with more complex behavior; for example, if the source model provides a custom hasChildren() implementation, you should also provide one in the proxy model.
See also QAbstractProxyModel, QAbstractItemModel, Model/View Programming, Basic Sort/Filter Model Example, and Custom Sort/Filter Model Example.
Property Documentation
dynamicSortFilter : bool
This property holds whether the proxy model is dynamically sorted and filtered whenever the contents of the source model change.
The default value is false.
This property was introduced in Qt 4.2.
Access functions:
- bool dynamicSortFilter () const
- void setDynamicSortFilter ( bool enable )
filterCaseSensitivity : Qt::CaseSensitivity
This property holds the case sensitivity of the QRegExp pattern used to filter the contents of the source model.
By default, the filter is case sensitive.
Access functions:
- Qt::CaseSensitivity filterCaseSensitivity () const
- void setFilterCaseSensitivity ( Qt::CaseSensitivity cs )
See also filterRegExp and sortCaseSensitivity.
filterKeyColumn : int
This property holds the column where the key used to filter the contents of the source model is read from.
The default value is 0. If the value is -1, the keys will be read from all columns.
Access functions:
- int filterKeyColumn () const
- void setFilterKeyColumn ( int column )
filterRegExp : QRegExp
This property holds the QRegExp used to filter the contents of the source model.
Setting this property overwrites the current filterCaseSensitivity. By default, the QRegExp is an empty string matching all contents.
Access functions:
- QRegExp filterRegExp () const
- void setFilterRegExp ( const QRegExp & regExp )
- void setFilterRegExp ( const QString & pattern )
See also filterCaseSensitivity, setFilterWildcard(), and setFilterFixedString().
filterRole : int
This property holds the item role that is used to query the source model's data when filtering items.
The default value is Qt::DisplayRole.
This property was introduced in Qt 4.2.
Access functions:
- int filterRole () const
- void setFilterRole ( int role )
See also filterAcceptsRow().
isSortLocaleAware : bool
This property holds the local aware setting used for comparing strings when sorting.
By default, sorting is not local aware.
This property was introduced in Qt 4.3.
Access functions:
- bool isSortLocaleAware () const
- void setSortLocaleAware ( bool on )
See also sortCaseSensitivity and lessThan().
sortCaseSensitivity : Qt::CaseSensitivity
This property holds the case sensitivity setting used for comparing strings when sorting.
By default, sorting is case sensitive.
This property was introduced in Qt 4.2.
Access functions:
- Qt::CaseSensitivity sortCaseSensitivity () const
- void setSortCaseSensitivity ( Qt::CaseSensitivity cs )
See also filterCaseSensitivity and lessThan().
sortRole : int
This property holds the item role that is used to query the source model's data when sorting items.
The default value is Qt::DisplayRole.
This property was introduced in Qt 4.2.
Access functions:
- int sortRole () const
- void setSortRole ( int role )
See also lessThan().
Member Function Documentation
QSortFilterProxyModel::QSortFilterProxyModel ( QObject * parent = 0 )
Constructs a sorting filter model with the given parent.
QSortFilterProxyModel::~QSortFilterProxyModel ()
Destroys this sorting filter model.
bool QSortFilterProxyModel::filterAcceptsColumn ( int source_column, const QModelIndex & source_parent ) const [virtual protected]
Returns true if the item in the column indicated by the given source_column and source_parent should be included in the model; otherwise returns false.
The default implementation returns true if the value held by the relevant item matches the filter string, wildcard string or regular expression.
Note: By default, the Qt::DisplayRole is used to determine if the row should be accepted or not. This can be changed by setting the filterRole property.
See also filterAcceptsRow(), setFilterFixedString(), setFilterRegExp(), and setFilterWildcard().
bool QSortFilterProxyModel::filterAcceptsRow ( int source_row, const QModelIndex & source_parent ) const [virtual protected]
Returns true if the item in the row indicated by the given source_row and source_parent should be included in the model; otherwise returns false.
The default implementation returns true if the value held by the relevant item matches the filter string, wildcard string or regular expression.
Note: By default, the Qt::DisplayRole is used to determine if the row should be accepted or not. This can be changed by setting the filterRole property.
See also filterAcceptsColumn(), setFilterFixedString(), setFilterRegExp(), and setFilterWildcard().
void QSortFilterProxyModel::invalidate () [slot]
Invalidates the current sorting and filtering.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.3.
See also invalidateFilter().
void QSortFilterProxyModel::invalidateFilter () [protected]
Invalidates the current filtering.
This function should be called if you are implementing custom filtering (e.g. filterAcceptsRow()), and your filter parameters have changed.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.3.
See also invalidate().
bool QSortFilterProxyModel::lessThan ( const QModelIndex & left, const QModelIndex & right ) const [virtual protected]
Returns true if the value of the item referred to by the given index left is less than the value of the item referred to by the given index right, otherwise returns false.
This function is used as the < operator when sorting, and handles the following QVariant types:
- QVariant::Int
- QVariant::UInt
- QVariant::LongLong
- QVariant::ULongLong
- QVariant::Double
- QVariant::Char
- QVariant::Date
- QVariant::Time
- QVariant::DateTime
- QVariant::String
Any other type will be converted to a QString using QVariant::toString().
Comparison of QStrings is case sensitive by default; this can be changed using the sortCaseSensitivity property.
By default, the Qt::DisplayRole associated with the QModelIndexes is used for comparisons. This can be changed by setting the sortRole property.
Note: The indices passed in correspond to the source model.
See also sortRole, sortCaseSensitivity, and dynamicSortFilter.
QModelIndex QSortFilterProxyModel::mapFromSource ( const QModelIndex & sourceIndex ) const [virtual]
Returns the model index in the QSortFilterProxyModel given the sourceIndex from the source model.
Reimplemented from QAbstractProxyModel.
See also mapToSource().
QModelIndex QSortFilterProxyModel::mapToSource ( const QModelIndex & proxyIndex ) const [virtual]
Returns the source model index corresponding to the given proxyIndex from the sorting filter model.
Reimplemented from QAbstractProxyModel.
See also mapFromSource().
void QSortFilterProxyModel::setFilterFixedString ( const QString & pattern ) [slot]
Sets the fixed string used to filter the contents of the source model to the given pattern.
See also setFilterCaseSensitivity(), setFilterRegExp(), setFilterWildcard(), and filterRegExp().
void QSortFilterProxyModel::setFilterWildcard ( const QString & pattern ) [slot]
Sets the wildcard expression used to filter the contents of the source model to the given pattern.
See also setFilterCaseSensitivity(), setFilterRegExp(), setFilterFixedString(), and filterRegExp().
int QSortFilterProxyModel::sortColumn () const
the column currently used for sorting
This returns the most recently used sort column.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.5.
Qt::SortOrder QSortFilterProxyModel::sortOrder () const
the order currently used for sorting
This returns the most recently used sort order.
This function was introduced in Qt 4.5.
Best Of
Actualités les plus lues
- «Le projet de loi des droits du développeur» : quelles conditions doivent remplir les entreprises pour que le développeur puisse réussir ? 73
- Les développeurs détestent-ils les antivirus ? Un programmeur manifeste sa haine envers ces solutions de sécurité 27
- Une nouvelle ère d'IHM 3D pour les automobiles, un concept proposé par Digia et implémenté avec Qt 3
- Qt Creator 2.5 est sorti en beta, l'EDI supporte maintenant plus de fonctionnalités de C++11 2
- Vingt sociétés montrent leurs décodeurs basés sur Qt au IPTV World Forum, en en exploitant diverses facettes (déclaratif, Web, widgets) 0
- PySide devient un add-on Qt et rejoint le Qt Project et le modèle d'open gouvernance 1
- Thread travailleur avec Qt en utilisant les signaux et les slots, un article de Christophe Dumez traduit par Thibaut Cuvelier 1
- « Quelque chose ne va vraiment pas avec les développeurs "modernes" », un développeur à "l'ancienne" critique la multiplication des bibliothèques 102
- Pourquoi les programmeurs sont-ils moins payés que les gestionnaires de programmes ? Manquent-ils de pouvoir de négociation ? 53
- «Le projet de loi des droits du développeur» : quelles conditions doivent remplir les entreprises pour que le développeur puisse réussir ? 73
- Les développeurs détestent-ils les antivirus ? Un programmeur manifeste sa haine envers ces solutions de sécurité 27
- Qt Commercial : Digia organise un webinar gratuit le 27 mars sur la conception d'interfaces utilisateur et d'applications avec le framework 0
- Quelles nouveautés de C++11 Visual C++ doit-il rapidement intégrer ? Donnez-nous votre avis 10
- 2017 : un quinquennat pour une nouvelle version du C++ ? Possible, selon Herb Sutter 11

- Linus Torvalds : le "C++ est un langage horrible", en justifiant le choix du C pour le système de gestion de version Git 100
- Comment prendre en compte l'utilisateur dans vos applications ? Pour un développeur, « 90 % des utilisateurs sont des idiots » 229
- Quel est LE livre que tout développeur doit lire absolument ? Celui qui vous a le plus marqué et inspiré 96
- Apple cède et s'engage à payer des droits à Nokia, le conflit des brevets entre les deux firmes s'achève 158
- Nokia porte à nouveau plainte contre Apple pour violation de sept nouveaux brevets 158
- Quel est le code dont vous êtes le plus fier ? Pourquoi l'avez-vous écrit ? Et pourquoi vous a-t-il donné autant de satisfaction ? 83
- « Quelque chose ne va vraiment pas avec les développeurs "modernes" », un développeur à "l'ancienne" critique la multiplication des bibliothèques 101

Le Qt Developer Network au hasard

Comment créer une fenêtre À propos
Communauté
Ressources
- 91 cours et tutoriels Qt
- F.A.Q. Qt : 200 questions et réponses
- 51 Qt Quarterly, 35 Qt Labs et 22 Qt DevNet en français
- 43 outils Qt
- 99 sources Qt et 26 binaires Qt
- 6 livres Qt et 9 critiques
- La documentation de Qt 4.7 en français : 157 classes, 70 concepts et 24 modules
- 3 certifications Qt
Liens utiles
Contact
- Vous souhaitez rejoindre la rédaction ou proposer un tutoriel, une traduction, une question... ? Postez dans le forum Contribuez ou contactez-nous par MP ou par email (voir en bas de page).
Qt dans le magazine
| Cette page est une traduction d'une page de la documentation de Qt, écrite par Nokia Corporation and/or its subsidiary(-ies). Les éventuels problèmes résultant d'une mauvaise traduction ne sont pas imputables à Nokia. | Qt 4.5 | |
| Copyright © 2012 Developpez LLC. Tous droits réservés Developpez LLC. Aucune reproduction, même partielle, ne peut être faite de ce site et de l'ensemble de son contenu : textes, documents et images sans l'autorisation expresse de Developpez LLC. Sinon, vous encourez selon la loi jusqu'à 3 ans de prison et jusqu'à 300 000 E de dommages et intérêts. Cette page est déposée à la SACD. | ||
| Vous avez déniché une erreur ? Un bug ? Une redirection cassée ? Ou tout autre problème, quel qu'il soit ? Ou bien vous désirez participer à ce projet de traduction ? N'hésitez pas à nous contacter ou par MP ! | ||
Copyright © 2000-2012 - www.developpez.com



















