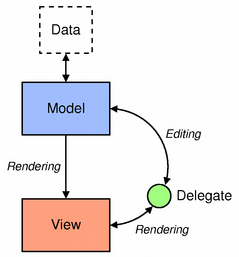
Model/View ProgrammingIntroduction to Model/View ProgrammingQt 4 introduced a new set of item view classes that use a model/view architecture to manage the relationship between data and the way it is presented to the user. The separation of functionality introduced by this architecture gives developers greater flexibility to customize the presentation of items, and provides a standard model interface to allow a wide range of data sources to be used with existing item views. In this document, we give a brief introduction to the model/view paradigm, outline the concepts involved, and describe the architecture of the item view system. Each of the components in the architecture is explained, and examples are given that show how to use the classes provided. The model/view architectureModel-View-Controller (MVC) is a design pattern originating from Smalltalk that is often used when building user interfaces. In Design Patterns, Gamma et al. write:
If the view and the controller objects are combined, the result is the model/view architecture. This still separates the way that data is stored from the way that it is presented to the user, but provides a simpler framework based on the same principles. This separation makes it possible to display the same data in several different views, and to implement new types of views, without changing the underlying data structures. To allow flexible handling of user input, we introduce the concept of the delegate. The advantage of having a delegate in this framework is that it allows the way items of data are rendered and edited to be customized.
Generally, the model/view classes can be separated into the three groups described above: models, views, and delegates. Each of these components is defined by abstract classes that provide common interfaces and, in some cases, default implementations of features. Abstract classes are meant to be subclassed in order to provide the full set of functionality expected by other components; this also allows specialized components to be written. Models, views, and delegates communicate with each other using signals and slots:
ModelsAll item models are based on the QAbstractItemModel class. This class defines an interface that is used by views and delegates to access data. The data itself does not have to be stored in the model; it can be held in a data structure or repository provided by a separate class, a file, a database, or some other application component. The basic concepts surrounding models are presented in the section on Model Classes. QAbstractItemModel provides an interface to data that is flexible enough to handle views that represent data in the form of tables, lists, and trees. However, when implementing new models for list and table-like data structures, the QAbstractListModel and QAbstractTableModel classes are better starting points because they provide appropriate default implementations of common functions. Each of these classes can be subclassed to provide models that support specialized kinds of lists and tables. The process of subclassing models is discussed in the section on Creating New Models. Qt provides some ready-made models that can be used to handle items of data:
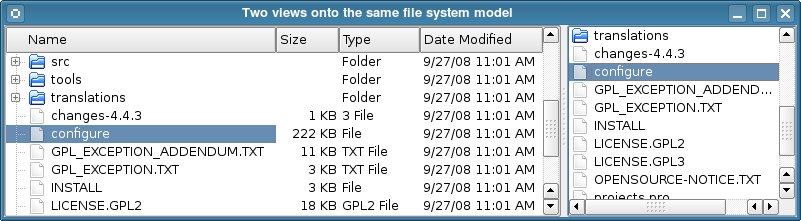
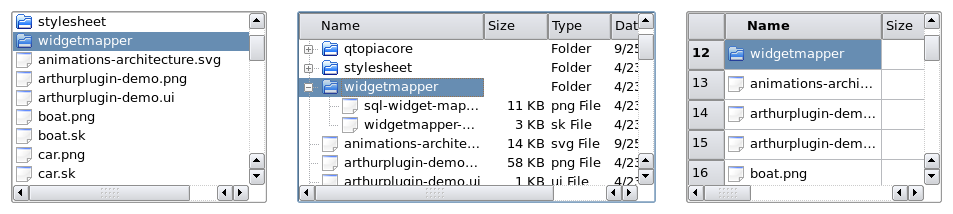
If these standard models do not meet your requirements, you can subclass QAbstractItemModel, QAbstractListModel, or QAbstractTableModel to create your own custom models. ViewsComplete implementations are provided for different kinds of views: QListView displays a list of items, QTableView displays data from a model in a table, and QTreeView shows model items of data in a hierarchical list. Each of these classes is based on the QAbstractItemView abstract base class. Although these classes are ready-to-use implementations, they can also be subclassed to provide customized views. The available views are examined in the section on View Classes. DelegatesQAbstractItemDelegate is the abstract base class for delegates in the model/view framework. Since Qt 4.4, the default delegate implementation is provided by QStyledItemDelegate, and this is used as the default delegate by Qt's standard views. However, QStyledItemDelegate and QItemDelegate are independent alternatives to painting and providing editors for items in views. The difference between them is that QStyledItemDelegate uses the current style to paint its items. We therefore recommend using QStyledItemDelegate as the base class when implementing custom delegates or when working with Qt style sheets. Delegates are described in the section on Delegate Classes. SortingThere are two ways of approaching sorting in the model/view architecture; which approach to choose depends on your underlying model. If your model is sortable, i.e, if it reimplements the QAbstractItemModel::sort() function, both QTableView and QTreeView provide an API that allows you to sort your model data programmatically. In addition, you can enable interactive sorting (i.e. allowing the users to sort the data by clicking the view's headers), by connecting the QHeaderView::sortIndicatorChanged() signal to the QTableView::sortByColumn() slot or the QTreeView::sortByColumn() slot, respectively. The alternative approach, if your model do not have the required interface or if you want to use a list view to present your data, is to use a proxy model to transform the structure of your model before presenting the data in the view. This is covered in detail in the section on Proxy Models. Convenience classesA number of convenience classes are derived from the standard view classes for the benefit of applications that rely on Qt's item-based item view and table classes. They are not intended to be subclassed, but simply exist to provide a familiar interface to the equivalent classes in Qt 3. Examples of such classes include QListWidget, QTreeWidget, and QTableWidget; these provide similar behavior to the QListBox, QListView, and QTable classes in Qt 3. These classes are less flexible than the view classes, and cannot be used with arbitrary models. We recommend that you use a model/view approach to handling data in item views unless you strongly need an item-based set of classes. If you wish to take advantage of the features provided by the model/view approach while still using an item-based interface, consider using view classes, such as QListView, QTableView, and QTreeView with QStandardItemModel. Using models and viewsThe following sections explain how to use the model/view pattern in Qt. Each section includes an an example and is followed by a section showing how to create new components. Two models included in QtTwo of the standard models provided by Qt are QStandardItemModel and QFileSystemModel. QStandardItemModel is a multi-purpose model that can be used to represent various different data structures needed by list, table, and tree views. This model also holds the items of data. QFileSystemModel is a model that maintains information about the contents of a directory. As a result, it does not hold any items of data itself, but simply represents files and directories on the local filing system. QFileSystemModel provides a ready-to-use model to experiment with, and can be easily configured to use existing data. Using this model, we can show how to set up a model for use with ready-made views, and explore how to manipulate data using model indexes. Using views with an existing modelThe QListView and QTreeView classes are the most suitable views to use with QFileSystemModel. The example presented below displays the contents of a directory in a tree view next to the same information in a list view. The views share the user's selection so that the selected items are highlighted in both views.
We set up a QFileSystemModel so that it is ready for use, and create some views to display the contents of a directory. This shows the simplest way to use a model. The construction and use of the model is performed from within a single main() function: int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { QApplication app(argc, argv); QSplitter *splitter = new QSplitter; QFileSystemModel *model = new QFileSystemModel; model->setRootPath(QDir::currentPath()); The model is set up to use data from a certain file system. The call to setRootPath() tell the model which drive on the file system to expose to the views. We create two views so that we can examine the items held in the model in two different ways: QTreeView *tree = new QTreeView(splitter); tree->setModel(model); tree->setRootIndex(model->index(QDir::currentPath())); QListView *list = new QListView(splitter); list->setModel(model); list->setRootIndex(model->index(QDir::currentPath())); The views are constructed in the same way as other widgets. Setting up a view to display the items in the model is simply a matter of calling its setModel() function with the directory model as the argument. We filter the data supplied by the model by calling the setRootIndex() function on each view, passing a suitable model index from the file system model for the current directory. The index() function used in this case is unique to QFileSystemModel; we supply it with a directory and it returns a model index. Model indexes are discussed in Model Classes. The rest of the function just displays the views within a splitter widget, and runs the application's event loop: splitter->setWindowTitle("Two views onto the same file system model"); splitter->show(); return app.exec(); } In the above example, we neglected to mention how to handle selections of items. This subject is covered in more detail in the section about Handling Selections in Item Views. Model classesBefore examining how selections are handled, you may find it useful to examine the concepts used in the model/view framework. Basic conceptsIn the model/view architecture, the model provides a standard interface that views and delegates use to access data. In Qt, the standard interface is defined by the QAbstractItemModel class. No matter how the items of data are stored in any underlying data structure, all subclasses of QAbstractItemModel represent the data as a hierarchical structure containing tables of items. Views use this convention to access items of data in the model, but they are not restricted in the way that they present this information to the user.
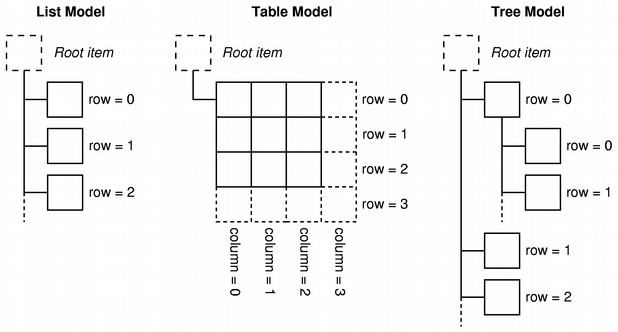
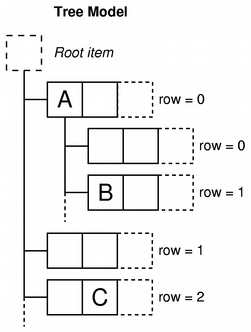
Models also notify any attached views about changes to data through the signals and slots mechanism. This section describes some basic concepts that are central to the way item of data are accessed by other components via a model class. More advanced concepts are discussed in later sections. Model indexesTo ensure that the representation of the data is kept separate from the way it is accessed, the concept of a model index is introduced. Each piece of information that can be obtained via a model is represented by a model index. Views and delegates use these indexes to request items of data to display. As a result, only the model needs to know how to obtain data, and the type of data managed by the model can be defined fairly generally. Model indexes contain a pointer to the model that created them, and this prevents confusion when working with more than one model. QAbstractItemModel *model = index.model(); Model indexes provide temporary references to pieces of information, and can be used to retrieve or modify data via the model. Since models may reorganize their internal structures from time to time, model indexes may become invalid, and should not be stored. If a long-term reference to a piece of information is required, a persistent model index must be created. This provides a reference to the information that the model keeps up-to-date. Temporary model indexes are provided by the QModelIndex class, and persistent model indexes are provided by the QPersistentModelIndex class. To obtain a model index that corresponds to an item of data, three properties must be specified to the model: a row number, a column number, and the model index of a parent item. The following sections describe and explain these properties in detail. Rows and columnsIn its most basic form, a model can be accessed as a simple table in which items are located by their row and column numbers. This does not mean that the underlying pieces of data are stored in an array structure; the use of row and column numbers is only a convention to allow components to communicate with each other. We can retrieve information about any given item by specifying its row and column numbers to the model, and we receive an index that represents the item: QModelIndex index = model->index(row, column, ...); Models that provide interfaces to simple, single level data structures like lists and tables do not need any other information to be provided but, as the above code indicates, we need to supply more information when obtaining a model index.
Parents of itemsThe table-like interface to item data provided by models is ideal when using data in a table or list view; the row and column number system maps exactly to the way the views display items. However, structures such as tree views require the model to expose a more flexible interface to the items within. As a result, each item can also be the parent of another table of items, in much the same way that a top-level item in a tree view can contain another list of items. When requesting an index for a model item, we must provide some information about the item's parent. Outside the model, the only way to refer to an item is through a model index, so a parent model index must also be given: QModelIndex index = model->index(row, column, parent);
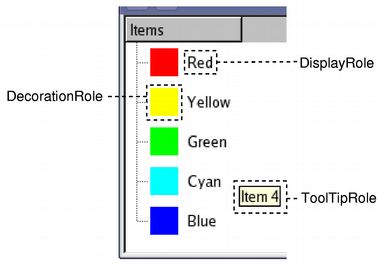
Item rolesItems in a model can perform various roles for other components, allowing different kinds of data to be supplied for different situations. For example, Qt::DisplayRole is used to access a string that can be displayed as text in a view. Typically, items contain data for a number of different roles, and the standard roles are defined by Qt::ItemDataRole. We can ask the model for the item's data by passing it the model index corresponding to the item, and by specifying a role to obtain the type of data we want: QVariant value = model->data(index, role);
Most common uses for item data are covered by the standard roles defined in Qt::ItemDataRole. By supplying appropriate item data for each role, models can provide hints to views and delegates about how items should be presented to the user. Different kinds of views have the freedom to interpret or ignore this information as required. It is also possible to define additional roles for application-specific purposes. Summary
Using model indexesTo demonstrate how data can be retrieved from a model, using model indexes, we set up a QFileSystemModel without a view and display the names of files and directories in a widget. Although this does not show a normal way of using a model, it demonstrates the conventions used by models when dealing with model indexes. We construct a file system model in the following way: QFileSystemModel *model = new QFileSystemModel; QModelIndex parentIndex = model->index(QDir::currentPath()); int numRows = model->rowCount(parentIndex); In this case, we set up a default QFileSystemModel, obtain a parent index using a specific implementation of index() provided by that model, and we count the number of rows in the model using the rowCount() function. For simplicity, we are only interested in the items in the first column of the model. We examine each row in turn, obtaining a model index for the first item in each row, and read the data stored for that item in the model. for (int row = 0; row < numRows; ++row) { QModelIndex index = model->index(row, 0, parentIndex); To obtain a model index, we specify the row number, column number (zero for the first column), and the appropriate model index for the parent of all the items that we want. The text stored in each item is retrieved using the model's data() function. We specify the model index and the DisplayRole to obtain data for the item in the form of a string. QString text = model->data(index, Qt::DisplayRole).toString(); // Display the text in a widget. } The above example demonstrates the basic principles used to retrieve data from a model:
Further readingNew models can be created by implementing the standard interface provided by QAbstractItemModel. In the Creating New Models section, we demonstrate this by creating a convenient ready-to-use model for holding lists of strings. View classesConceptsIn the model/view architecture, the view obtains items of data from the model and presents them to the user. The way that the data is presented need not resemble the representation of the data provided by the model, and may be completely different from the underlying data structure used to store items of data. The separation of content and presentation is achieved by the use of a standard model interface provided by QAbstractItemModel, a standard view interface provided by QAbstractItemView, and the use of model indexes that represent items of data in a general way. Views typically manage the overall layout of the data obtained from models. They may render individual items of data themselves, or use delegates to handle both rendering and editing features. As well as presenting data, views handle navigation between items, and some aspects of item selection. The views also implement basic user interface features, such as context menus and drag and drop. A view can provide default editing facilities for items, or it may work with a delegate to provide a custom editor. A view can be constructed without a model, but a model must be provided before it can display useful information. Views keep track of the items that the user has selected through the use of selections which can be maintained separately for each view, or shared between multiple views. Some views, such as QTableView and QTreeView, display headers as well as items. These are also implemented by a view class, QHeaderView. Headers usually access the same model as the view that contains them. They retrieve data from the model using the QAbstractItemModel::headerData() function, and usually display header information in the form of a label. New headers can be subclassed from the QHeaderView class to provide more specialized labels for views. Using an existing viewQt provides three ready-to-use view classes that present data from models in ways that are familiar to most users. QListView can display items from a model as a simple list, or in the form of a classic icon view. QTreeView displays items from a model as a hierarchy of lists, allowing deeply nested structures to be represented in a compact way. QTableView presents items from a model in the form of a table, much like the layout of a spreadsheet application.
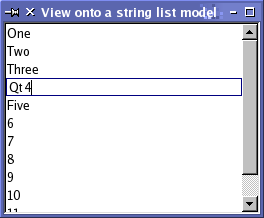
The default behavior of the standard views shown above should be sufficient for most applications. They provide basic editing facilities, and can be customized to suit the needs of more specialized user interfaces. Using a modelWe take the string list model that we created as an example model, set it up with some data, and construct a view to display the contents of the model. This can all be performed within a single function: int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { QApplication app(argc, argv); // Unindented for quoting purposes: QStringList numbers; numbers << "One" << "Two" << "Three" << "Four" << "Five"; QAbstractItemModel *model = new StringListModel(numbers); Note that the StringListModel is declared as a QAbstractItemModel. This allows us to use the abstract interface to the model, and ensures that the code still works, even if we replace the string list model with a different model. The list view provided by QListView is sufficient for presenting the items in the string list model. We construct the view, and set up the model using the following lines of code: QListView *view = new QListView; view->setModel(model); The view is shown in the normal way: view->show(); return app.exec(); } The view renders the contents of a model, accessing data via the model's interface. When the user tries to edit an item, the view uses a default delegate to provide an editor widget.
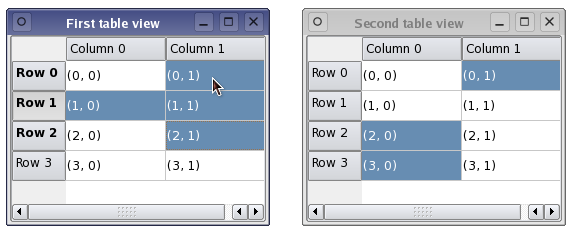
The above image shows how a QListView represents the data in the string list model. Since the model is editable, the view automatically allows each item in the list to be edited using the default delegate. Using multiple views of a modelProviding multiple views onto the same model is simply a matter of setting the same model for each view. In the following code we create two table views, each using the same simple table model which we have created for this example: QTableView *firstTableView = new QTableView; QTableView *secondTableView = new QTableView; firstTableView->setModel(model); secondTableView->setModel(model); The use of signals and slots in the model/view architecture means that changes to the model can be propagated to all the attached views, ensuring that we can always access the same data regardless of the view being used.
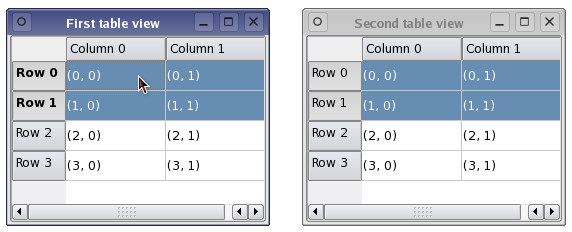
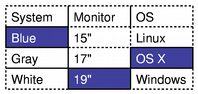
The above image shows two different views onto the same model, each containing a number of selected items. Although the data from the model is shown consistently across view, each view maintains its own internal selection model. This can be useful in certain situations but, for many applications, a shared selection model is desirable. Handling selections of itemsThe mechanism for handling selections of items within views is provided by the QItemSelectionModel class. All of the standard views construct their own selection models by default, and interact with them in the normal way. The selection model being used by a view can be obtained through the selectionModel() function, and a replacement selection model can be specified with setSelectionModel(). The ability to control the selection model used by a view is useful when we want to provide multiple consistent views onto the same model data. Generally, unless you are subclassing a model or view, you don't need to manipulate the contents of selections directly. However, the interface to the selection model can be accessed, if required, and this is explored in Handling Selections in Item Views. Sharing selections among viewsAlthough it is convenient that the view classes provide their own selection models by default, when we use more than one view onto the same model it is often desirable that both the model's data and the user's selection are shown consistently in all views. Since the view classes allow their internal selection models to be replaced, we can achieve a unified selection between views with the following line: secondTableView->setSelectionModel(firstTableView->selectionModel()); The second view is given the selection model for the first view. Both views now operate on the same selection model, keeping both the data and the selected items synchronized.
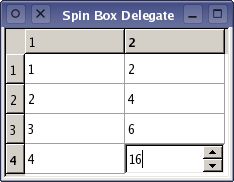
In the example shown above, two views of the same type were used to display the same model's data. However, if two different types of view were used, the selected items may be represented very differently in each view; for example, a contiguous selection in a table view can be represented as a fragmented set of highlighted items in a tree view. Delegate classesConceptsUnlike the Model-View-Controller pattern, the model/view design does not include a completely separate component for managing interaction with the user. Generally, the view is responsible for the presentation of model data to the user, and for processing user input. To allow some flexibility in the way this input is obtained, the interaction is performed by delegates. These components provide input capabilities and are also responsible for rendering individual items in some views. The standard interface for controlling delegates is defined in the QAbstractItemDelegate class. Delegates are expected to be able to render their contents themselves by implementing the paint() and sizeHint() functions. However, simple widget-based delegates can subclass QItemDelegate instead of QAbstractItemDelegate, and take advantage of the default implementations of these functions. Editors for delegates can be implemented either by using widgets to manage the editing process or by handling events directly. The first approach is covered later in this section, and it is also shown in the Spin Box Delegate example. The Pixelator example shows how to create a custom delegate that performs specialized rendering for a table view. Using an existing delegateThe standard views provided with Qt use instances of QItemDelegate to provide editing facilities. This default implementation of the delegate interface renders items in the usual style for each of the standard views: QListView, QTableView, and QTreeView. All the standard roles are handled by the default delegate used by the standard views. The way these are interpreted is described in the QItemDelegate documentation. The delegate used by a view is returned by the itemDelegate() function. The setItemDelegate() function allows you to install a custom delegate for a standard view, and it is necessary to use this function when setting the delegate for a custom view. A simple delegateThe delegate implemented here uses a QSpinBox to provide editing facilities, and is mainly intended for use with models that display integers. Although we set up a custom integer-based table model for this purpose, we could easily have used QStandardItemModel instead, since the custom delegate controls data entry. We construct a table view to display the contents of the model, and this will use the custom delegate for editing.
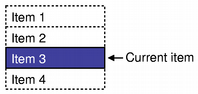
We subclass the delegate from QItemDelegate because we do not want to write custom display functions. However, we must still provide functions to manage the editor widget: class SpinBoxDelegate : public QItemDelegate { Q_OBJECT public: SpinBoxDelegate(QObject *parent = 0); QWidget *createEditor(QWidget *parent, const QStyleOptionViewItem &option, const QModelIndex &index) const; void setEditorData(QWidget *editor, const QModelIndex &index) const; void setModelData(QWidget *editor, QAbstractItemModel *model, const QModelIndex &index) const; void updateEditorGeometry(QWidget *editor, const QStyleOptionViewItem &option, const QModelIndex &index) const; }; Note that no editor widgets are set up when the delegate is constructed. We only construct an editor widget when it is needed. Providing an editorIn this example, when the table view needs to provide an editor, it asks the delegate to provide an editor widget that is appropriate for the item being modified. The createEditor() function is supplied with everything that the delegate needs to be able to set up a suitable widget: QWidget *SpinBoxDelegate::createEditor(QWidget *parent, const QStyleOptionViewItem &/* option */, const QModelIndex &/* index */) const { QSpinBox *editor = new QSpinBox(parent); editor->setMinimum(0); editor->setMaximum(100); return editor; } Note that we do not need to keep a pointer to the editor widget because the view takes responsibility for destroying it when it is no longer needed. We install the delegate's default event filter on the editor to ensure that it provides the standard editing shortcuts that users expect. Additional shortcuts can be added to the editor to allow more sophisticated behavior; these are discussed in the section on Editing Hints. The view ensures that the editor's data and geometry are set correctly by calling functions that we define later for these purposes. We can create different editors depending on the model index supplied by the view. For example, if we have a column of integers and a column of strings we could return either a QSpinBox or a QLineEdit, depending on which column is being edited. The delegate must provide a function to copy model data into the editor. In this example, we read the data stored in the display role, and set the value in the spin box accordingly. void SpinBoxDelegate::setEditorData(QWidget *editor, const QModelIndex &index) const { int value = index.model()->data(index, Qt::EditRole).toInt(); QSpinBox *spinBox = static_cast<QSpinBox*>(editor); spinBox->setValue(value); } In this example, we know that the editor widget is a spin box, but we could have provided different editors for different types of data in the model, in which case we would need to cast the widget to the appropriate type before accessing its member functions. Submitting data to the modelWhen the user has finished editing the value in the spin box, the view asks the delegate to store the edited value in the model by calling the setModelData() function. void SpinBoxDelegate::setModelData(QWidget *editor, QAbstractItemModel *model, const QModelIndex &index) const { QSpinBox *spinBox = static_cast<QSpinBox*>(editor); spinBox->interpretText(); int value = spinBox->value(); model->setData(index, value, Qt::EditRole); } Since the view manages the editor widgets for the delegate, we only need to update the model with the contents of the editor supplied. In this case, we ensure that the spin box is up-to-date, and update the model with the value it contains using the index specified. The standard QItemDelegate class informs the view when it has finished editing by emitting the closeEditor() signal. The view ensures that the editor widget is closed and destroyed. In this example, we only provide simple editing facilities, so we need never emit this signal. All the operations on data are performed through the interface provided by QAbstractItemModel. This makes the delegate mostly independent from the type of data it manipulates, but some assumptions must be made in order to use certain types of editor widgets. In this example, we have assumed that the model always contains integer values, but we can still use this delegate with different kinds of models because QVariant provides sensible default values for unexpected data. Updating the editor's geometryIt is the responsibility of the delegate to manage the editor's geometry. The geometry must be set when the editor is created, and when the item's size or position in the view is changed. Fortunately, the view provides all the necessary geometry information inside a view option object. void SpinBoxDelegate::updateEditorGeometry(QWidget *editor, const QStyleOptionViewItem &option, const QModelIndex &/* index */) const { editor->setGeometry(option.rect); } In this case, we just use the geometry information provided by the view option in the item rectangle. A delegate that renders items with several elements would not use the item rectangle directly. It would position the editor in relation to the other elements in the item. Editing hintsAfter editing, delegates should provide hints to the other components about the result of the editing process, and provide hints that will assist any subsequent editing operations. This is achieved by emitting the closeEditor() signal with a suitable hint. This is taken care of by the default QItemDelegate event filter which we installed on the spin box when it was constructed. The behavior of the spin box could be adjusted to make it more user friendly. In the default event filter supplied by QItemDelegate, if the user hits Return to confirm their choice in the spin box, the delegate commits the value to the model and closes the spin box. We can change this behavior by installing our own event filter on the spin box, and provide editing hints that suit our needs; for example, we might emit closeEditor() with the EditNextItem hint to automatically start editing the next item in the view. Another approach that does not require the use of an event filter is to provide our own editor widget, perhaps subclassing QSpinBox for convenience. This alternative approach would give us more control over how the editor widget behaves at the cost of writing additional code. It is usually easier to install an event filter in the delegate if you need to customize the behavior of a standard Qt editor widget. Delegates do not have to emit these hints, but those that do not will be less integrated into applications, and will be less usable than those that emit hints to support common editing actions. Handling selections in item viewsConceptsThe selection model used in the item view classes offers many improvements over the selection model used in Qt 3. It provides a more general description of selections based on the facilities of the model/view architecture. Although the standard classes for manipulating selections are sufficient for the item views provided, the selection model allows you to create specialized selection models to suit the requirements for your own item models and views. Information about the items selected in a view is stored in an instance of the QItemSelectionModel class. This maintains model indexes for items in a single model, and is independent of any views. Since there can be many views onto a model, it is possible to share selections between views, allowing applications to show multiple views in a consistent way. Selections are made up of selection ranges. These efficiently maintain information about large selections of items by recording only the starting and ending model indexes for each range of selected items. Non-contiguous selections of items are constructed by using more than one selection range to describe the selection. Selections are applied to a collection of model indexes held by a selection model. The most recent selection of items applied is known as the current selection. The effects of this selection can be modified even after its application through the use of certain types of selection commands. These are discussed later in this section. Current item and selected itemsIn a view, there is always a current item and a selected item - two independent states. An item can be the current item and selected at the same time. The view is responsible for ensuring that there is always a current item as keyboard navigation, for example, requires a current item. The table below highlights the differences between current item and selected items.
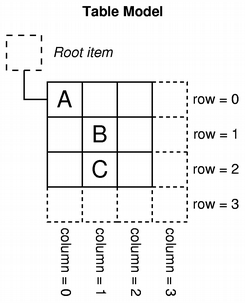
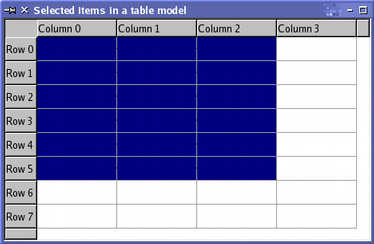
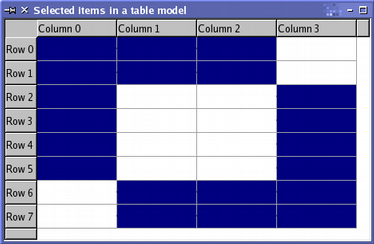
When manipulating selections, it is often helpful to think of QItemSelectionModel as a record of the selection state of all the items in an item model. Once a selection model is set up, collections of items can be selected, deselected, or their selection states can be toggled without the need to know which items are already selected. The indexes of all selected items can be retrieved at any time, and other components can be informed of changes to the selection model via the signals and slots mechanism. Using a selection modelThe standard view classes provide default selection models that can be used in most applications. A selection model belonging to one view can be obtained using the view's selectionModel() function, and shared between many views with setSelectionModel(), so the construction of new selection models is generally not required. A selection is created by specifying a model, and a pair of model indexes to a QItemSelection. This uses the indexes to refer to items in the given model, and interprets them as the top-left and bottom-right items in a block of selected items. To apply the selection to items in a model requires the selection to be submitted to a selection model; this can be achieved in a number of ways, each having a different effect on the selections already present in the selection model. Selecting itemsTo demonstrate some of the principal features of selections, we construct an instance of a custom table model with 32 items in total, and open a table view onto its data: TableModel *model = new TableModel(8, 4, &app); QTableView *table = new QTableView(0); table->setModel(model); QItemSelectionModel *selectionModel = table->selectionModel(); The table view's default selection model is retrieved for later use. We do not modify any items in the model, but instead select a few items that the view will display at the top-left of the table. To do this, we need to retrieve the model indexes corresponding to the top-left and bottom-right items in the region to be selected: QModelIndex topLeft; QModelIndex bottomRight; topLeft = model->index(0, 0, QModelIndex()); bottomRight = model->index(5, 2, QModelIndex()); To select these items in the model, and see the corresponding change in the table view, we need to construct a selection object then apply it to the selection model: QItemSelection selection(topLeft, bottomRight); selectionModel->select(selection, QItemSelectionModel::Select); The selection is applied to the selection model using a command defined by a combination of selection flags. In this case, the flags used cause the items recorded in the selection object to be included in the selection model, regardless of their previous state. The resulting selection is shown by the view.
The selection of items can be modified using various operations that are defined by the selection flags. The selection that results from these operations may have a complex structure, but it is represented efficiently by the selection model. The use of different selection flags to manipulate the selected items is described when we examine how to update a selection. Reading the selection stateThe model indexes stored in the selection model can be read using the selectedIndexes() function. This returns an unsorted list of model indexes that we can iterate over as long as we know which model they are for: QModelIndexList indexes = selectionModel->selectedIndexes(); QModelIndex index; foreach(index, indexes) { QString text = QString("(%1,%2)").arg(index.row()).arg(index.column()); model->setData(index, text); } The above code uses Qt's convenient foreach keyword to iterate over, and modify, the items corresponding to the indexes returned by the selection model. The selection model emits signals to indicate changes in the selection. These notify other components about changes to both the selection as a whole and the currently focused item in the item model. We can connect the selectionChanged() signal to a slot, and examine the items in the model that are selected or deselected when the selection changes. The slot is called with two QItemSelection objects: one contains a list of indexes that correspond to newly selected items; the other contains indexes that correspond to newly deselected items. In the following code, we provide a slot that receives the selectionChanged() signal, fills in the selected items with a string, and clears the contents of the deselected items. void MainWindow::updateSelection(const QItemSelection &selected, const QItemSelection &deselected) { QModelIndex index; QModelIndexList items = selected.indexes(); foreach (index, items) { QString text = QString("(%1,%2)").arg(index.row()).arg(index.column()); model->setData(index, text); } items = deselected.indexes(); foreach (index, items) model->setData(index, ""); } We can keep track of the currently focused item by connecting the currentChanged() signal to a slot that is called with two model indexes. These correspond to the previously focused item, and the currently focused item. In the following code, we provide a slot that receives the currentChanged() signal, and uses the information provided to update the status bar of a QMainWindow: void MainWindow::changeCurrent(const QModelIndex ¤t, const QModelIndex &previous) { statusBar()->showMessage( tr("Moved from (%1,%2) to (%3,%4)") .arg(previous.row()).arg(previous.column()) .arg(current.row()).arg(current.column())); } Monitoring selections made by the user is straightforward with these signals, but we can also update the selection model directly. Updating a selectionSelection commands are provided by a combination of selection flags, defined by QItemSelectionModel::SelectionFlag. Each selection flag tells the selection model how to update its internal record of selected items when either of the select() functions are called. The most commonly used flag is the Select flag which instructs the selection model to record the specified items as being selected. The Toggle flag causes the selection model to invert the state of the specified items, selecting any deselected items given, and deselecting any currently selected items. The Deselect flag deselects all the specified items. Individual items in the selection model are updated by creating a selection of items, and applying them to the selection model. In the following code, we apply a second selection of items to the table model shown above, using the Toggle command to invert the selection state of the items given. QItemSelection toggleSelection; topLeft = model->index(2, 1, QModelIndex()); bottomRight = model->index(7, 3, QModelIndex()); toggleSelection.select(topLeft, bottomRight); selectionModel->select(toggleSelection, QItemSelectionModel::Toggle); The results of this operation are displayed in the table view, providing a convenient way of visualizing what we have achieved:
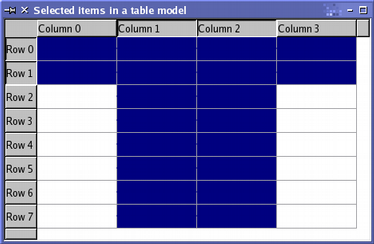
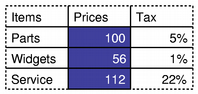
By default, the selection commands only operate on the individual items specified by the model indexes. However, the flag used to describe the selection command can be combined with additional flags to change entire rows and columns. For example if you call select() with only one index, but with a command that is a combination of Select and Rows, the entire row containing the item referred to is selected. The following code demonstrates the use of the Rows and Columns flags: QItemSelection columnSelection; topLeft = model->index(0, 1, QModelIndex()); bottomRight = model->index(0, 2, QModelIndex()); columnSelection.select(topLeft, bottomRight); selectionModel->select(columnSelection, QItemSelectionModel::Select | QItemSelectionModel::Columns); QItemSelection rowSelection; topLeft = model->index(0, 0, QModelIndex()); bottomRight = model->index(1, 0, QModelIndex()); rowSelection.select(topLeft, bottomRight); selectionModel->select(rowSelection, QItemSelectionModel::Select | QItemSelectionModel::Rows); Although only four indexes are supplied to the selection model, the use of the Columns and Rows selection flags means that two columns and two rows are selected. The following image shows the result of these two selections:
The commands performed on the example model have all involved accumulating a selection of items in the model. It is also possible to clear the selection, or to replace the current selection with a new one. To replace the current selection with a new selection, combine the other selection flags with the Current flag. A command using this flag instructs the selection model to replace its current collection of model indexes with those specified in a call to select(). To clear all selections before you start adding new ones, combine the other selection flags with the Clear flag. This has the effect of resetting the selection model's collection of model indexes. Selecting all items in a modelTo select all items in a model, it is necessary to create a selection for each level of the model that covers all items in that level. We do this by retrieving the indexes corresponding to the top-left and bottom-right items with a given parent index: QModelIndex topLeft = model->index(0, 0, parent); QModelIndex bottomRight = model->index(model->rowCount(parent)-1, model->columnCount(parent)-1, parent); A selection is constructed with these indexes and the model. The corresponding items are then selected in the selection model: QItemSelection selection(topLeft, bottomRight); selectionModel->select(selection, QItemSelectionModel::Select); This needs to be performed for all levels in the model. For top-level items, we would define the parent index in the usual way: QModelIndex parent = QModelIndex(); For hierarchical models, the hasChildren() function is used to determine whether any given item is the parent of another level of items. Creating new modelsThe separation of functionality between the model/view components allows models to be created that can take advantage of existing views. This approach lets us present data from a variety of sources using standard graphical user interface components, such as QListView, QTableView, and QTreeView. The QAbstractItemModel class provides an interface that is flexible enough to support data sources that arrange information in hierarchical structures, allowing for the possibility that data will be inserted, removed, modified, or sorted in some way. It also provides support for drag and drop operations. The QAbstractListModel and QAbstractTableModel classes provide support for interfaces to simpler non-hierarchical data structures, and are easier to use as a starting point for simple list and table models. In this section, we create a simple read-only model to explore the basic principles of the model/view architecture. Later in this section, we adapt this simple model so that items can be modified by the user. For an example of a more complex model, see the Simple Tree Model example. The requirements of QAbstractItemModel subclasses is described in more detail in the Model Subclassing Reference document. Designing a modelWhen creating a new model for an existing data structure, it is important to consider which type of model should be used to provide an interface onto the data. If the data structure can be represented as a list or table of items, you can subclass QAbstractListModel or QAbstractTableModel since these classes provide suitable default implementations for many functions. However, if the underlying data structure can only be represented by a hierarchical tree structure, it is necessary to subclass QAbstractItemModel. This approach is taken in the Simple Tree Model example. In this section, we implement a simple model based on a list of strings, so the QAbstractListModel provides an ideal base class on which to build. Whatever form the underlying data structure takes, it is usually a good idea to supplement the standard QAbstractItemModel API in specialized models with one that allows more natural access to the underlying data structure. This makes it easier to populate the model with data, yet still enables other general model/view components to interact with it using the standard API. The model described below provides a custom constructor for just this purpose. A read-only example modelThe model implemented here is a simple, non-hierarchical, read-only data model based on the standard QStringListModel class. It has a QStringList as its internal data source, and implements only what is needed to make a functioning model. To make the implementation easier, we subclass QAbstractListModel because it defines sensible default behavior for list models, and it exposes a simpler interface than the QAbstractItemModel class. When implementing a model it is important to remember that QAbstractItemModel does not store any data itself, it merely presents an interface that the views use to access the data. For a minimal read-only model it is only necessary to implement a few functions as there are default implementations for most of the interface. The class declaration is as follows: class StringListModel : public QAbstractListModel { Q_OBJECT public: StringListModel(const QStringList &strings, QObject *parent = 0) : QAbstractListModel(parent), stringList(strings) {} int rowCount(const QModelIndex &parent = QModelIndex()) const; QVariant data(const QModelIndex &index, int role) const; QVariant headerData(int section, Qt::Orientation orientation, int role = Qt::DisplayRole) const; private: QStringList stringList; }; Apart from the model's constructor, we only need to implement two functions: rowCount() returns the number of rows in the model and data() returns an item of data corresponding to a specified model index. Well behaved models also implement headerData() to give tree and table views something to display in their headers. Note that this is a non-hierarchical model, so we don't have to worry about the parent-child relationships. If our model was hierarchical, we would also have to implement the index() and parent() functions. The list of strings is stored internally in the stringList private member variable. Dimensions of the modelWe want the number of rows in the model to be the same as the number of strings in the string list. We implement the rowCount() function with this in mind: int StringListModel::rowCount(const QModelIndex &parent) const { return stringList.count(); } Since the model is non-hierarchical, we can safely ignore the model index corresponding to the parent item. By default, models derived from QAbstractListModel only contain one column, so we do not need to reimplement the columnCount() function. Model headers and dataFor items in the view, we want to return the strings in the string list. The data() function is responsible for returning the item of data that corresponds to the index argument: QVariant StringListModel::data(const QModelIndex &index, int role) const { if (!index.isValid()) return QVariant(); if (index.row() >= stringList.size()) return QVariant(); if (role == Qt::DisplayRole) return stringList.at(index.row()); else return QVariant(); } We only return a valid QVariant if the model index supplied is valid, the row number is within the range of items in the string list, and the requested role is one that we support. Some views, such as QTreeView and QTableView, are able to display headers along with the item data. If our model is displayed in a view with headers, we want the headers to show the row and column numbers. We can provide information about the headers by subclassing the headerData() function: QVariant StringListModel::headerData(int section, Qt::Orientation orientation, int role) const { if (role != Qt::DisplayRole) return QVariant(); if (orientation == Qt::Horizontal) return QString("Column %1").arg(section); else return QString("Row %1").arg(section); } Again, we return a valid QVariant only if the role is one that we support. The orientation of the header is also taken into account when deciding the exact data to return. Not all views display headers with the item data, and those that do may be configured to hide them. Nonetheless, it is recommended that you implement the headerData() function to provide relevant information about the data provided by the model. An item can have several roles, giving out different data depending on the role specified. The items in our model only have one role, DisplayRole, so we return the data for items irrespective of the role specified. However, we could reuse the data we provide for the DisplayRole in other roles, such as the ToolTipRole that views can use to display information about items in a tooltip. An editable modelThe read-only model shows how simple choices could be presented to the user but, for many applications, an editable list model is much more useful. We can modify the read-only model to make the items editable by changing the data() function we implemented for read-only, and by implementing two extra functions: flags() and setData(). The following function declarations are added to the class definition: Qt::ItemFlags flags(const QModelIndex &index) const; bool setData(const QModelIndex &index, const QVariant &value, int role = Qt::EditRole); Making the model editableA delegate checks whether an item is editable before creating an editor. The model must let the delegate know that its items are editable. We do this by returning the correct flags for each item in the model; in this case, we enable all items and make them both selectable and editable: Qt::ItemFlags StringListModel::flags(const QModelIndex &index) const { if (!index.isValid()) return Qt::ItemIsEnabled; return QAbstractItemModel::flags(index) | Qt::ItemIsEditable; } Note that we do not have to know how the delegate performs the actual editing process. We only have to provide a way for the delegate to set the data in the model. This is achieved through the setData() function: bool StringListModel::setData(const QModelIndex &index, const QVariant &value, int role) { if (index.isValid() && role == Qt::EditRole) { stringList.replace(index.row(), value.toString()); emit dataChanged(index, index); return true; } return false; } In this model, the item in the string list that corresponds to the model index is replaced by the value provided. However, before we can modify the string list, we must make sure that the index is valid, the item is of the correct type, and that the role is supported. By convention, we insist that the role is the EditRole since this is the role used by the standard item delegate. For boolean values, however, you can use Qt::CheckStateRole and set the Qt::ItemIsUserCheckable flag; a checkbox is then used for editing the value. The underlying data in this model is the same for all roles, so this detail just makes it easier to integrate the model with standard components. When the data has been set, the model must let the views know that some data has changed. This is done by emitting the dataChanged() signal. Since only one item of data has changed, the range of items specified in the signal is limited to just one model index. Also the data() function needs to be changed to add the Qt::EditRole test: QVariant StringListModel::data(const QModelIndex &index, int role) const { if (!index.isValid()) return QVariant(); if (index.row() >= stringList.size()) return QVariant(); if (role == Qt::DisplayRole || role == Qt::EditRole) return stringList.at(index.row()); else return QVariant(); } Inserting and removing rowsIt is possible to change the number of rows and columns in a model. In the string list model it only makes sense to change the number of rows, so we only reimplement the functions for inserting and removing rows. These are declared in the class definition: bool insertRows(int position, int rows, const QModelIndex &index = QModelIndex()); bool removeRows(int position, int rows, const QModelIndex &index = QModelIndex()); Since rows in this model correspond to strings in a list, the insertRows() function inserts a number of empty strings into the string list before the specified position. The number of strings inserted is equivalent to the number of rows specified. The parent index is normally used to determine where in the model the rows should be added. In this case, we only have a single top-level list of strings, so we just insert empty strings into that list. bool StringListModel::insertRows(int position, int rows, const QModelIndex &parent) { beginInsertRows(QModelIndex(), position, position+rows-1); for (int row = 0; row < rows; ++row) { stringList.insert(position, ""); } endInsertRows(); return true; } The model first calls the beginInsertRows() function to inform other components that the number of rows is about to change. The function specifies the row numbers of the first and last new rows to be inserted, and the model index for their parent item. After changing the string list, it calls endInsertRows() to complete the operation and inform other components that the dimensions of the model have changed, returning true to indicate success. The function to remove rows from the model is also simple to write. The rows to be removed from the model are specified by the position and the number of rows given. We ignore the parent index to simplify our implementation, and just remove the corresponding items from the string list. bool StringListModel::removeRows(int position, int rows, const QModelIndex &parent) { beginRemoveRows(QModelIndex(), position, position+rows-1); for (int row = 0; row < rows; ++row) { stringList.removeAt(position); } endRemoveRows(); return true; } The beginRemoveRows() function is always called before any underlying data is removed, and specifies the first and last rows to be removed. This allows other components to access the data before it becomes unavailable. After the rows have been removed, the model emits endRemoveRows() to finish the operation and let other components know that the dimensions of the model have changed. Next stepsWe can display the data provided by this model, or any other model, using the QListView class to present the model's items in the form of a vertical list. For the string list model, this view also provides a default editor so that the items can be manipulated. We examine the possibilities made available by the standard view classes in View Classes. The Model Subclassing Reference document discusses the requirements of QAbstractItemModel subclasses in more detail, and provides a guide to the virtual functions that must be implemented to enable various features in different types of models. Item view convenience classesQt 4 also introduced some standard widgets to provide classic item-based container widgets. These behave in a similar way to the item view classes in Qt 3, but have been rewritten to use the underlying model/view framework for performance and maintainability. The old item view classes are still available in the compatibility library (see the Porting Guide for more information). The item-based widgets have been given names which reflect their uses: QListWidget provides a list of items, QTreeWidget displays a multi-level tree structure, and QTableWidget provides a table of cell items. Each class inherits the behavior of the QAbstractItemView class which implements common behavior for item selection and header management. List widgetsSingle level lists of items are typically displayed using a QListWidget and a number of QListWidgetItems. A list widget is constructed in the same way as any other widget: QListWidget *listWidget = new QListWidget(this); List items can be added directly to the list widget when they are constructed: new QListWidgetItem(tr("Sycamore"), listWidget); new QListWidgetItem(tr("Chestnut"), listWidget); new QListWidgetItem(tr("Mahogany"), listWidget); They can also be constructed without a parent list widget and added to a list at some later time: QListWidgetItem *newItem = new QListWidgetItem; newItem->setText(itemText); listWidget->insertItem(row, newItem); Each item in a list can display a text label and an icon. The colors and font used to render the text can be changed to provide a customized appearance for items. Tooltips, status tips, and "What's This?" help are all easily configured to ensure that the list is properly integrated into the application. newItem->setToolTip(toolTipText); newItem->setStatusTip(toolTipText); newItem->setWhatsThis(whatsThisText); By default, items in a list are presented in the order of their creation. Lists of items can be sorted according to the criteria given in Qt::SortOrder to produce a list of items that is sorted in forward or reverse alphabetical order: listWidget->sortItems(Qt::AscendingOrder); listWidget->sortItems(Qt::DescendingOrder); Tree widgetsTrees or hierarchical lists of items are provided by the QTreeWidget and QTreeWidgetItem classes. Each item in the tree widget can have child items of its own, and can display a number of columns of information. Tree widgets are created just like any other widget: QTreeWidget *treeWidget = new QTreeWidget(this); Before items can be added to the tree widget, the number of columns must be set. For example, we could define two columns, and create a header to provide labels at the top of each column: treeWidget->setColumnCount(2); QStringList headers; headers << tr("Subject") << tr("Default"); treeWidget->setHeaderLabels(headers); The easiest way to set up the labels for each section is to supply a string list. For more sophisticated headers, you can construct a tree item, decorate it as you wish, and use that as the tree widget's header. Top-level items in the tree widget are constructed with the tree widget as their parent widget. They can be inserted in an arbitrary order, or you can ensure that they are listed in a particular order by specifying the previous item when constructing each item: QTreeWidgetItem *cities = new QTreeWidgetItem(treeWidget); cities->setText(0, tr("Cities")); QTreeWidgetItem *osloItem = new QTreeWidgetItem(cities); osloItem->setText(0, tr("Oslo")); osloItem->setText(1, tr("Yes")); QTreeWidgetItem *planets = new QTreeWidgetItem(treeWidget, cities); Tree widgets deal with top-level items slightly differently to other items from deeper within the tree. Items can be removed from the top level of the tree by calling the tree widget's takeTopLevelItem() function, but items from lower levels are removed by calling their parent item's takeChild() function. Items are inserted in the top level of the tree with the insertTopLevelItem() function. At lower levels in the tree, the parent item's insertChild() function is used. It is easy to move items around between the top level and lower levels in the tree. We just need to check whether the items are top-level items or not, and this information is supplied by each item's parent() function. For example, we can remove the current item in the tree widget regardless of its location: QTreeWidgetItem *parent = currentItem->parent(); int index; if (parent) { index = parent->indexOfChild(treeWidget->currentItem()); delete parent->takeChild(index); } else { index = treeWidget->indexOfTopLevelItem(treeWidget->currentItem()); delete treeWidget->takeTopLevelItem(index); } Inserting the item somewhere else in the tree widget follows the same pattern: QTreeWidgetItem *parent = currentItem->parent(); QTreeWidgetItem *newItem; if (parent) newItem = new QTreeWidgetItem(parent, treeWidget->currentItem()); else newItem = new QTreeWidgetItem(treeWidget, treeWidget->currentItem()); Table widgetsTables of items similar to those found in spreadsheet applications are constructed with the QTableWidget and QTableWidgetItem. These provide a scrolling table widget with headers and items to use within it. Tables can be created with a set number of rows and columns, or these can be added to an unsized table as they are needed. QTableWidget *tableWidget; tableWidget = new QTableWidget(12, 3, this); Items are constructed outside the table before being added to the table at the required location: QTableWidgetItem *newItem = new QTableWidgetItem(tr("%1").arg( pow(row, column+1))); tableWidget->setItem(row, column, newItem); Horizontal and vertical headers can be added to the table by constructing items outside the table and using them as headers: QTableWidgetItem *valuesHeaderItem = new QTableWidgetItem(tr("Values")); tableWidget->setHorizontalHeaderItem(0, valuesHeaderItem); Note that the rows and columns in the table begin at zero. Common featuresThere are a number of item-based features common to each of the convenience classes that are available through the same interfaces in each class. We present these in the following sections with some examples for different widgets. Look at the list of Model/View Classes for each of the widgets for more details about the use of each function used. See also Item Views Puzzle Example. |