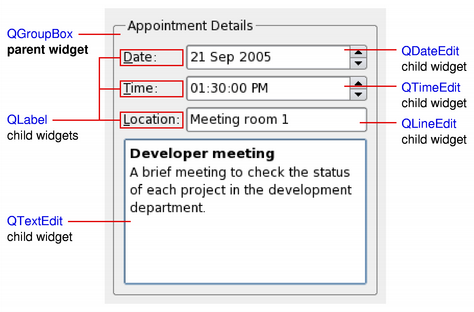
Widgets and LayoutsWidgetsWidgets are the primary elements for creating user interfaces in Qt. Widgets can display data and status information, receive user input, and provide a container for other widgets that should be grouped together. A widget that is not embedded in a parent widget is called a window.
The QWidget class provides the basic capability to render to the screen, and to handle user input events. All UI elements that Qt provides are either subclasses of QWidget, or are used in connection with a QWidget subclass. Creating custom widgets is done by subclassing QWidget or a suitable subclass and reimplementing the virtual event handlers. LayoutsLayouts are an elegant and flexible way to automatically arrange child widgets within their container. Each widget reports its size requirements to the layout through the sizeHint and sizePolicy properties, and the layout distributes the available space accordingly.
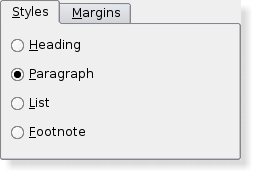
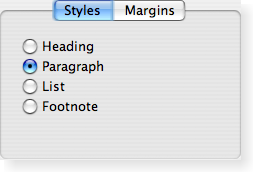
Qt Designer is a powerful tool for interactively creating and arranging widgets in layouts. Widget StylesStyles draw on behalf of widgets and encapsulate the look and feel of a GUI. Qt's built-in widgets use the QStyle class to perform nearly all of their drawing, ensuring that they look exactly like the equivalent native widgets.
Qt Style Sheets are a powerful mechanism that allows you to customize the appearance of widgets, in addition to what is already possible by subclassing QStyle. The Widget ClassesThe following sections list the widget classes. See the Qt Widget Gallery for some examples. Basic WidgetsThese basic widgets (controls), e.g. buttons, comboboxes and scroll bars, are designed for direct use.
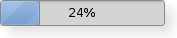
Advanced WidgetsAdvanced GUI widgets, e.g. tab widgets and progress bars, provide more complex user interface controls.
Organizer WidgetsClasses like splitters, tab bars, button groups, etc are used for organizing and grouping GUI primitives into more complex applications and dialogs.
Abstract Widget ClassesThe abstract widget classes are base classes. They are not usable as standalone classes but provide functionality when they are subclassed.
|