Using Version Control SystemsVersion control systems supported by Qt Creator are:
Setting Up Version Control SystemsQt Creator uses the version control system's command line clients to access your repositories. To allow access, make sure that the command line clients can be located using the PATH environment variable or specify the path to the command line client executables in Tools > Options... > Version Control. After you set up the version control system, use the command line to check that everything works (for example, use the status command). If no issues arise, you should be ready to use the system also from Qt Creator. Setting Up Common OptionsSelect Tools > Options... > Version Control > Common to specify settings for submit messages:
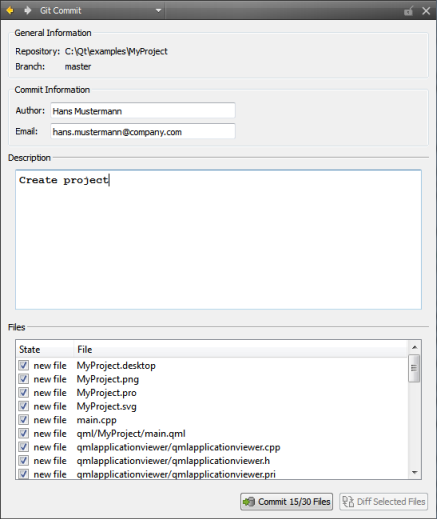
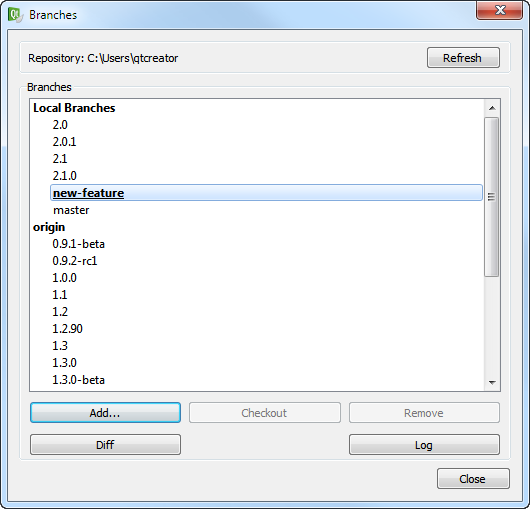
The fields above appear below the submit message. They provide completion for the aliases/public user names specified in the User/alias configuration file as well as a button that opens the aforementioned user name dialog. Creating VCS Repositories for New ProjectsQt Creator allows for creating VCS repositories for version control systems that support local repository creation, such as Git or Mercurial. When creating a new project by selecting File > New File or Project..., you can choose a version control system in the final wizard page. Using Version Control SystemsThe Tools menu contains a sub-menu for each supported version control system. The Version Control output pane displays the commands that are executed, a timestamp, and the relevant output. Select Window > Output Panes > Version Control to open the pane. When you create a new file or a new project, the wizard displays a page asking whether the files should be added to a version control system. This happens when the parent directory or the project is already under version control and the system supports the concept of adding files, for example, Perforce and Subversion. Alternatively, you can add files later by using the version control tool menus. With Git, there is no concept of adding files. Instead, all modified files must be staged for a commit. All version control systems provide menu options to diff the current file or project: to compare it with the latest version stored in the repository and to display the differences. In Qt Creator, a diff is displayed in a read-only editor. If the file is accessible, you can double-click on a selected diff chunk and Qt Creator opens an editor displaying the file, scrolled to the line in question. Display the versioning history of a file by selecting Log (for Git and Mercurial) or Filelog (for CVS, Perforce, and Subversion). Typically, the log output contains the date, the commit message, and a change or revision identifier. Click on the identifier to display a description of the change including the diff. Right-clicking on an identifier brings up a context menu that lets you show annotation views of previous versions (see Annotating Files). Annotation views are obtained by selecting Annotate or Blame. Selecting Annotate or Blame displays the lines of the file prepended by the change identifier they originate from. Clicking on the change identifier shows a detailed description of the change. To show the annotation of a previous version, right-click on the version identifier at the beginning of a line and choose one of the revisions shown at the bottom of the context menu. This allows you to navigate through the history of the file and obtain previous versions of it. It also works for Git and Mercurial using SHA's. The same context menu is available when right-clicking on a version identifier in the file log view of a single file. Once you have finished making changes, submit them to the version control system by choosing Commit or Submit. Qt Creator displays a commit page containing a text editor where you can enter your commit message and a checkable list of modified files to be included. When you have finished filling out the commit page information, click on Commit to start committing. The Diff Selected Files button brings up a diff view of the files selected in the file list. Since the commit page is just another editor, you can go back to it by closing the diff view. You can also check a diff view from the editor combo box showing the Opened files. To discard local changes to a file or project, use the Revert function or the Undo Changes/Undo Repository Changes function (for Git). The changes discarded depend on the version control system. For example, in Perforce, select Revert File/Revert Project to discard changes made to open files, reverting them to the revisions last synchronized from the repository. Select Revert Unchanged to revert files if their contents or file type have not changed after they were opened for editing. The Git sub-menu contains the following additional items: Apply Patch/Apply Patch... Apply changes to a file or project from a diff file. You can either apply a patch file that is open in Qt Creator or select the patch file to apply from the file system. Stash Snapshot... Save a snapshot of your current work under a name for later reference. For example, if you want to try out something and find out later that it does not work, you can discard it and return to the state of the snapshot. Stash Stash local changes prior to executing a Pull. Stash Pop Remove a single stashed state from the stash list and apply it on top of the current working tree state. Pull Pull changes from the remote repository. If there are locally modified files, you are prompted to stash those changes. The Git options page contains an option to do a rebase operation while pulling. Clean Repository.../Clean Project... Collect all files that are not under version control with the exception of patches and project files and show them as a checkable list in a dialog prompting for deletion. This lets you completely clean a build. Branches... Displays the branch dialog showing the local branches at the top and remote branches at the bottom. To switch to the local branch, double-click on it. Double-clicking on a remote branch first creates a local branch with the same name that tracks the remote branch, and then switches to it. Stashes... Displays a dialog showing the stashes created by Stash Snapshot... with options to restore, display or delete them. Stage File for Commit Mark new or modified files for committing to the repository. To undo this function, select Unstage File from Commit. Show Commit... Select a commit to view. Enter the SHA of the commit in the Change field. The Mercurial sub-menu contains the following additional items: Import Apply changes from a patch file. Incoming Monitor the status of a remote repository by listing the changes that will be pulled. Outgoing Monitor the status of a remote repository by listing the changes that will be pushed. Pull Pull changes from the remote repository. Update Look at an earlier version of the code. When you start Qt Creator, it looks for the executable specified in the P4 command field in Tools > Options... > Version Control > Perforce. If you do not use Perforce and want to turn off the check, clear this field. The Perforce sub-menu contains the following additional items: Describe... View information about changelists and the files in them. Edit File Open a file for editing. Opened List files that are open for editing. Pending Changes... Group files for commit. Update All/Update Current Project Fetch the current version of the current project or all projects from the repository. The Subversion sub-menu contains the following additional items: Describe... Display commit log messages for a revision. Update Project/Update Repository Update your working copy.
X
|