Creating Qt Quick Projects
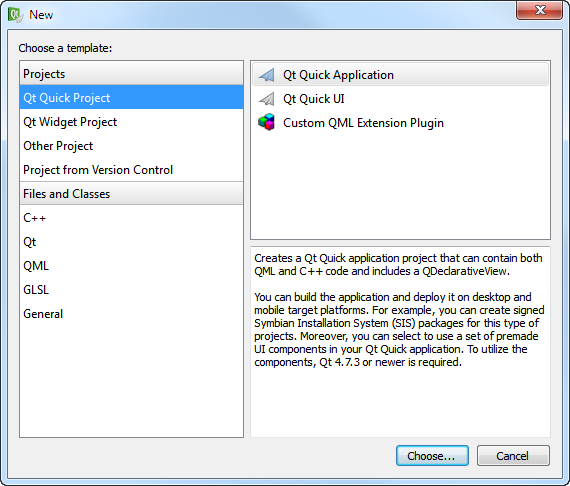
When you create a new Qt Quick project from scratch, you have the following options:
- Qt Quick Application creates a Qt Quick application project that can contain both QML and C++ code. The project includes a QDeclarativeView. You can build the application and deploy it on desktop and mobile target platforms. For example, you can create signed Symbian Installation System (SIS) packages for this type of projects.
- Qt Quick UI creates a Qt Quick UI project with a single QML file that contains the main view. You can review Qt Quick UI projects in the QML Viewer and you need not build them. You do not need to have the development environment installed on your computer to create and run this type of projects.
- Custom QML Extension Plugin creates a C++ plugin that makes it possible to offer extensions that can be loaded dynamically into applications by using the QDeclarativeEngine class.
If you have existing QML applications that you want to run in Qt Creator or deploy to mobile devices, use the Qt Quick Application wizard to convert them to Qt Quick applications.
Creating Qt Quick UI Projects
- Select File > New File or Project > Qt Quick Project > Qt Quick UI > Choose....
The Introduction and Project Location dialog opens.
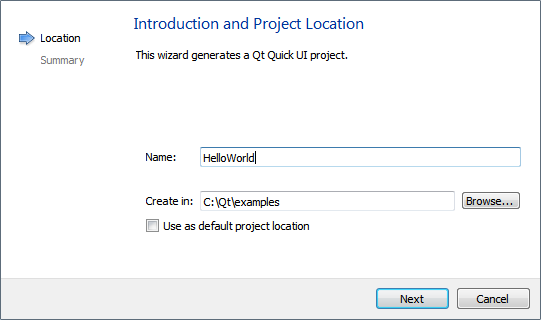
- In the Name field, give a name to the project.
Do not use spaces and special characters in the project name and path.
- In the Create in field, enter the path for the project files. For example, C:\Qt\examples. To select the path from a directory tree, click Browse.
- Click Next.
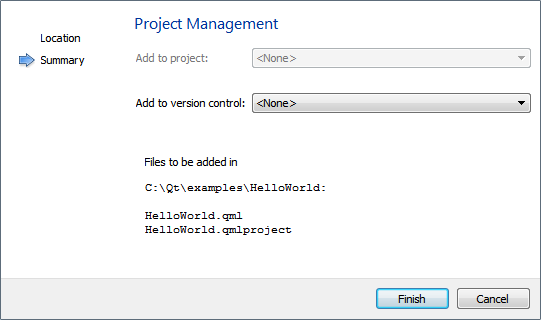
- Review the project settings, and click Finish to create the project.
Qt Creator creates the following files:
- .qmlproject project file defines that all QML, JavaScript, and image files in the project folder belong to the project. Therefore, you do not need to individually list all the files in the project.
- .qml file defines an element, such as a component, screen, or the whole application UI.
The import statement in the beginning of the .qml file specifies the Qt modules to import. Each Qt module contains a set of default elements. Specify a version to get the features you want.
To use JavaScript and image files in the application, copy them to the project folder.
Creating Qt Quick Applications
- Select File > New File or Project > Qt Quick Project > Qt Quick Application > Choose....
The Introduction and Project Location dialog opens.
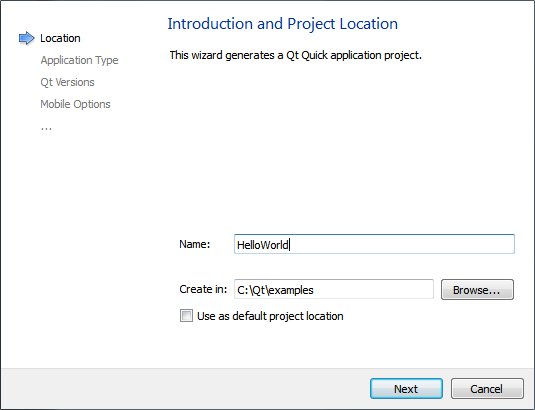
- In the Name field, give a name to the project.
Do not use spaces and special characters in the project name and path.
- In the Create in field, enter the path for the project files. For example, C:\Qt\examples. To select the path from a directory tree, click Browse.
- Click Next.
The Application Type dialog opens.
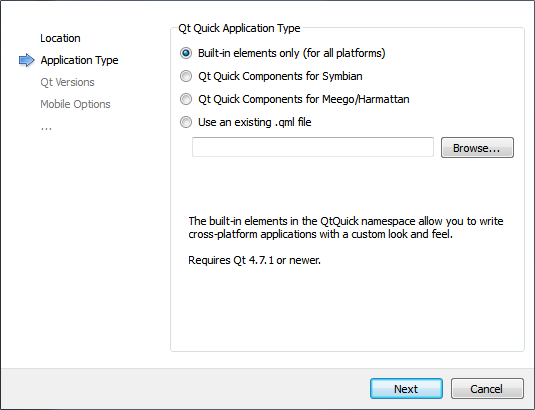
- Select the Qt Quick Component Set to use in your application. The built-in elements allow you to write cross-platform applications with custom look and feel. The components for Symbian and MeeGo Harmattan allow you to create applications with a native look and feel for the selected mobile platform.
You can also import an existing QML file in this dialog.
- Click Next.
The Target Setup dialog opens.
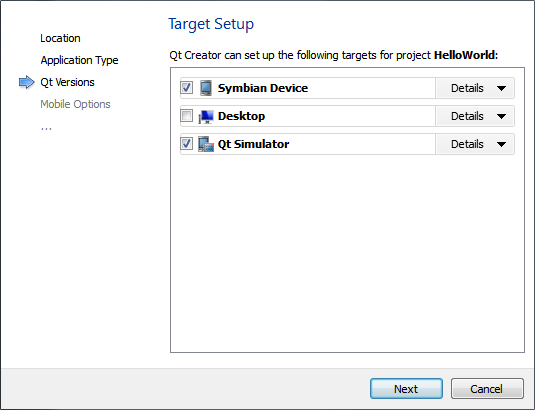
- Select the Qt versions to use as build targets for your project, and then click Next.
Note: Qt Quick is supported since Qt 4.7, and therefore, only Qt 4.7 and later versions are displayed. Further, if you have only one supported Qt version installed, this dialog is skipped.
The Mobile Options dialog opens.
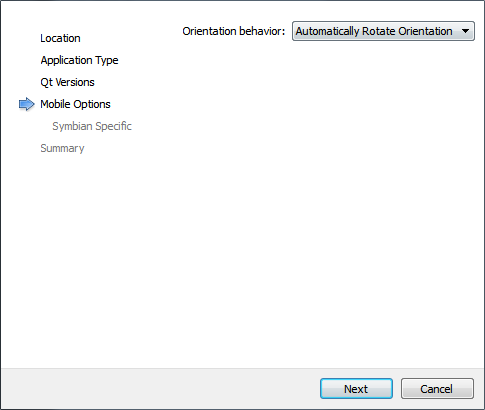
- In the Orientation behavior field, determine how the application behaves when the orientation of the device display rotates between portrait and landscape, and then click Next.
Note: This dialog opens only if you select Maemo5 or Symbian Device target in the Target Setup dialog. On Harmattan, the Qt Quick Components for MeeGo provide native-looking rotation.
The Symbian Specific dialog opens.
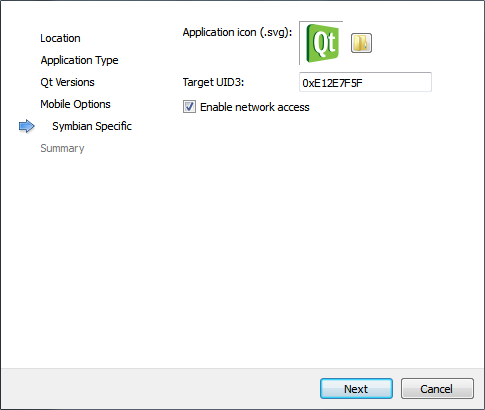
- In the Application icon (.svg) field, select an application icon for the Symbian Device target, or use the default icon.
- In the Target UID3 field, specify the Application UID, or use the default UID.
Note: Qt Creator generates a UID for testing the application on a device. You need to change the UID when you deliver the application for public use.
- Click Next.
The Maemo Specific dialog opens.
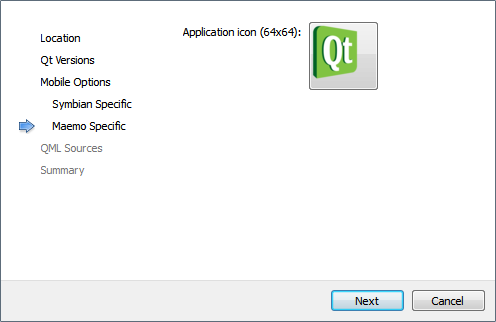
- In the Application icon field, select the application icon to use on Maemo or Harmattan targets, or use the default icon.
The Project Management dialog opens.
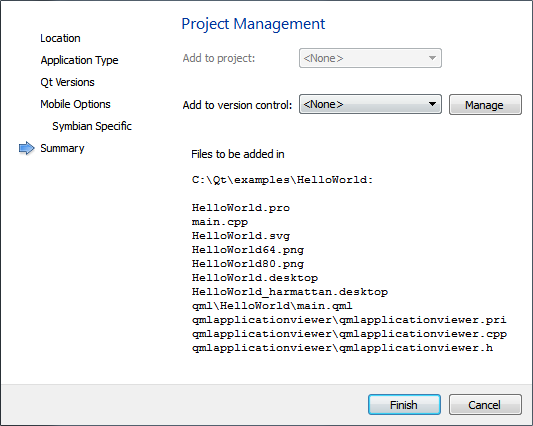
- In the Add to project field, you can add this project to another project as a subproject.
- In the Add to version control field, you can add the project to a version control system.
- Click Finish to create the project.
Qt Creator creates the necessary boilerplate files. Some of the files are specific to the Symbian, Maemo, or MeeGo Harmattan platform.
Importing QML Applications
If you have existing QML applications that you want to run in Qt Creator or deploy to mobile devices, use the Qt Quick Application wizard and select the main .qml file in your project. All the other files in the project are automatically added to the application project.
To import QML applications:
- Select File > New File or Project > Qt Quick Project > Qt Quick Application > Choose....
- Name the project and set its path, and then click Next.
- In the Application Type dialog, select the Use an existing .qml file option and specify the main .qml file of the project you want to import.
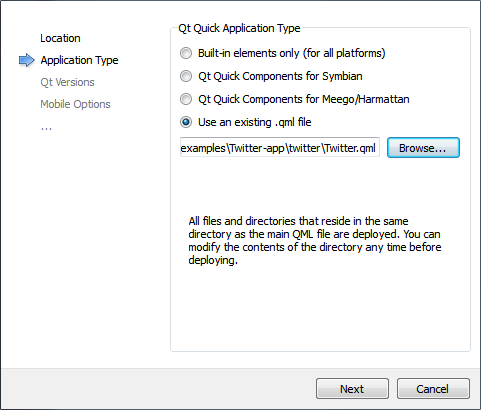
- Click Next.
- Select the Qt versions to use as build targets for your project, and click Next.
- Specify options for deploying the application to mobile device targets, and click Next.
- Review the project settings, and click Finish to create the project.
Qt Creator adds references to the QML files to a project and creates the additional files necessary for deploying applications to mobile devices.
|






























